Understanding the various types of software development is essential for choosing the right approach for your project's specific requirements.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the major categories of custom software development. Whether you're a decision-maker planning your company's digital transformation or a business leader seeking to understand development options for your next project, this article will provide the strategic insights you need.
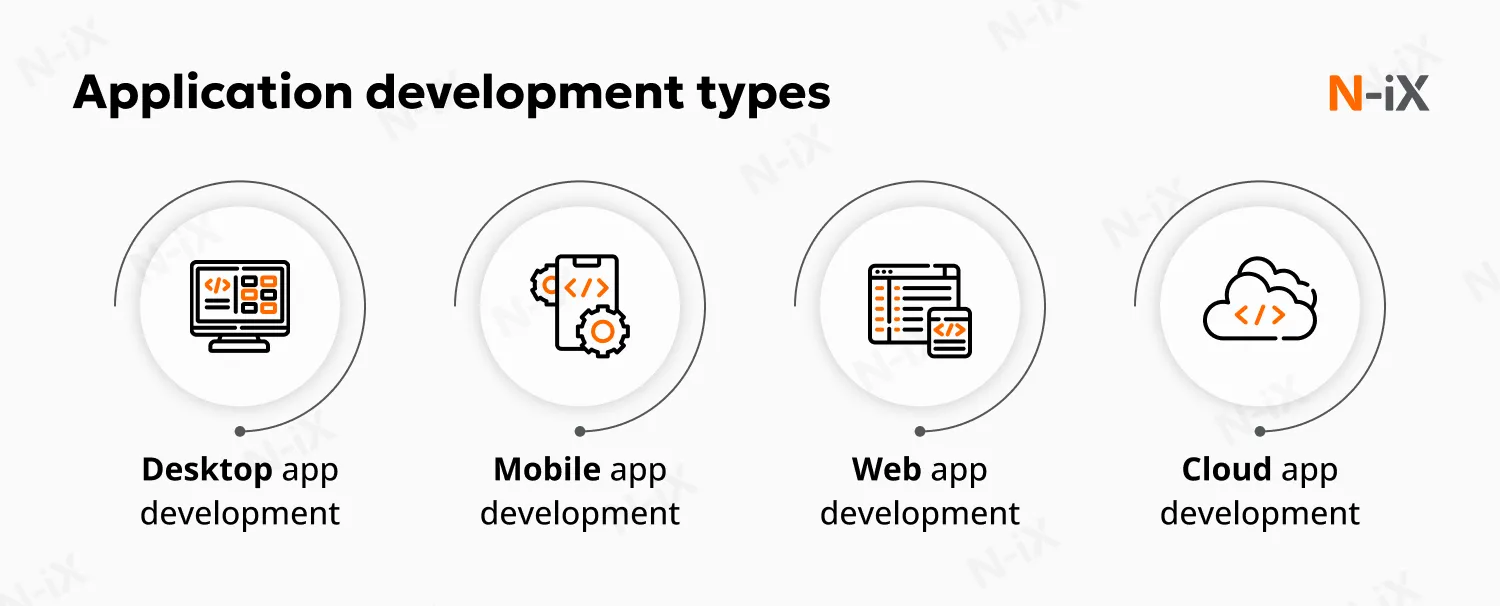
Application development: Building user-facing solutions
Application development represents perhaps the most visible form of software creation, focusing on programs that end-users interact with directly. This broad category encompasses several types of software development.
Desktop application development
These programs run natively on operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux, offering robust functionality and performance that web applications often struggle to match.
Desktop developers work with frameworks like Electron for cross-platform applications, .NET development for Windows-focused solutions, or native toolkits like Qt for high-performance applications. Industries such as creative software (Adobe Creative Suite), professional tools (AutoCAD), and gaming (Steam client) continue to rely heavily on desktop applications for their core functionality.
The appeal of desktop development lies in its ability to leverage the full power of the underlying hardware, access system-level features, and provide rich user interfaces.
Set your project up for success—get our 7-step guide to a discovery phase!


Success!

Mobile application development
Mobile development has transformed from a niche specialization to one of the most sought-after skills in software development. With billions of smartphones and tablets worldwide, mobile apps have become the primary interface between users and digital services.
Native mobile development involves creating platform-specific applications using languages like Swift for iOS or Kotlin/Java for Android development. This approach offers the best performance and access to platform-specific features but requires maintaining separate codebases for each platform.
Cross-platform frameworks like React Native, Flutter, and Xamarin have gained popularity by allowing developers to write code once and deploy to multiple platforms. While these solutions may not match the performance of native apps, they significantly reduce development time and maintenance overhead.
Web application development
Web development has evolved from simple static websites to complex applications that compete with desktop software in functionality. Modern web applications leverage sophisticated frameworks and technologies to deliver rich, interactive experiences directly through web browsers.
Frontend web development focuses on the user interface and user experience, utilizing technologies like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js. Strong frontend development directly impacts customer engagement and conversion rates, as users form judgments about a company's credibility within seconds of visiting their website. Investing in quality frontend development ensures a competitive advantage through superior user experiences that drive customer retention and business growth.
You may also be interested in: How to outsource web development: a comprehensive guide
Backend web development handles server-side logic, database interactions, and API development. Its developers work with languages like Python, Java, Node.js, or Go, databases, cloud services, and various architectural patterns. They're responsible for ensuring applications can scale to handle millions of users while maintaining security and reliability.
Full-stack web developers possess front-end and back-end development skills, making them versatile team members who can work across the entire web application stack. This breadth of knowledge makes full-stack development experts highly valuable, though they may not have the same depth of expertise as specialized frontend or backend developers.
Read more: How to outsource web development services efficiently?
Cloud application development
Cloud application development represents a software building method that uses cloud computing platforms and services. Unlike traditional applications that run on single servers, cloud applications are built to take advantage of distributed computing resources, automatic scaling, and managed services provided by platforms like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
Cloud developers focus on creating applications using cloud-native architectures such as microservices, serverless computing, and containerization. They work with services like managed databases, message queues, content delivery networks, and artificial intelligence APIs provided as cloud services rather than building these components from scratch.
Cloud development allows businesses to scale automatically based on demand, reduce infrastructure management overhead, and leverage advanced services that would be expensive to build independently. Cloud applications can handle sudden traffic spikes, automatically distribute load across multiple regions, and integrate sophisticated features like machine learning and real-time analytics with minimal additional development effort.
System development: Building the foundation
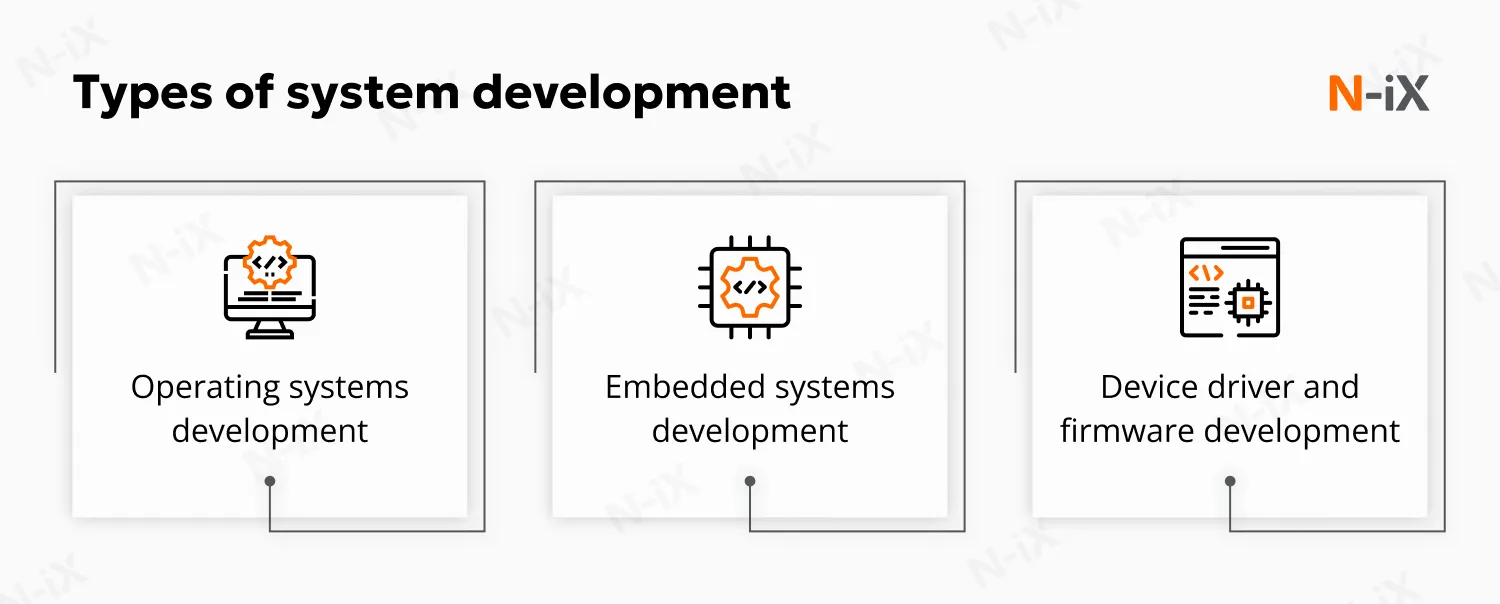
While application development focuses on user-facing software, system development involves creating the fundamental software that makes computers and networks function. It includes several types of software development that require deep technical knowledge and understanding of computer science principles.
Operating system development
Operating system development represents one of the most complex and challenging areas of software development. OS developers create the fundamental software layer that manages hardware resources, provides security, and enables other applications to run.
Modern operating system development involves kernel programming, device driver development, memory management, and process scheduling. Developers in this field typically work with low-level languages like C and assembly language, requiring extensive knowledge of computer architecture and hardware interfaces.
Custom operating systems enable companies to optimize resource usage, implement proprietary features, and maintain complete control over their technology stack, which is crucial for embedded systems, IoT devices, and enterprise environments with unique compliance or performance demands. Let's take a closer look.
Embedded systems and firmware development
Embedded software development involves creating software that runs on specialized hardware with specific constraints and requirements. These systems are everywhere, from household and automotive to medical devices and industrial equipment.
Embedded software development enables businesses to create smart, connected products that operate efficiently within strict hardware limitations while maintaining real-time responsiveness for critical applications. Companies leveraging embedded solutions can develop IoT devices, smart home products, wearable technology, and industrial sensors that provide competitive advantages through wireless connectivity, enhanced security, and edge computing capabilities that process data locally for faster decision-making.
Device driver and firmware development
Device drivers serve as the crucial interface between operating systems and hardware components. Driver developers create software that allows operating systems to communicate with graphics cards, network adapters, storage devices, and countless other hardware components. For hardware manufacturers, industrial automation companies, and businesses using specialized equipment, custom driver development ensures optimal performance, enables proprietary device functionality, and provides seamless integration of their specialized hardware into existing technology systems.
Firmware development is closely related to driver development, which involves creating the low-level software that runs directly on hardware components. While drivers facilitate communication between the OS and hardware, firmware controls the basic operations of the hardware at the most fundamental level. Firmware developers work on BIOS systems, embedded device controllers, and the core software that makes individual hardware components function.
For manufacturers of electronic devices, automotive systems, and industrial equipment, custom firmware development ensures reliable hardware operation, enables advanced product features, and provides the foundation for creating differentiated products that perform optimally in their intended applications.
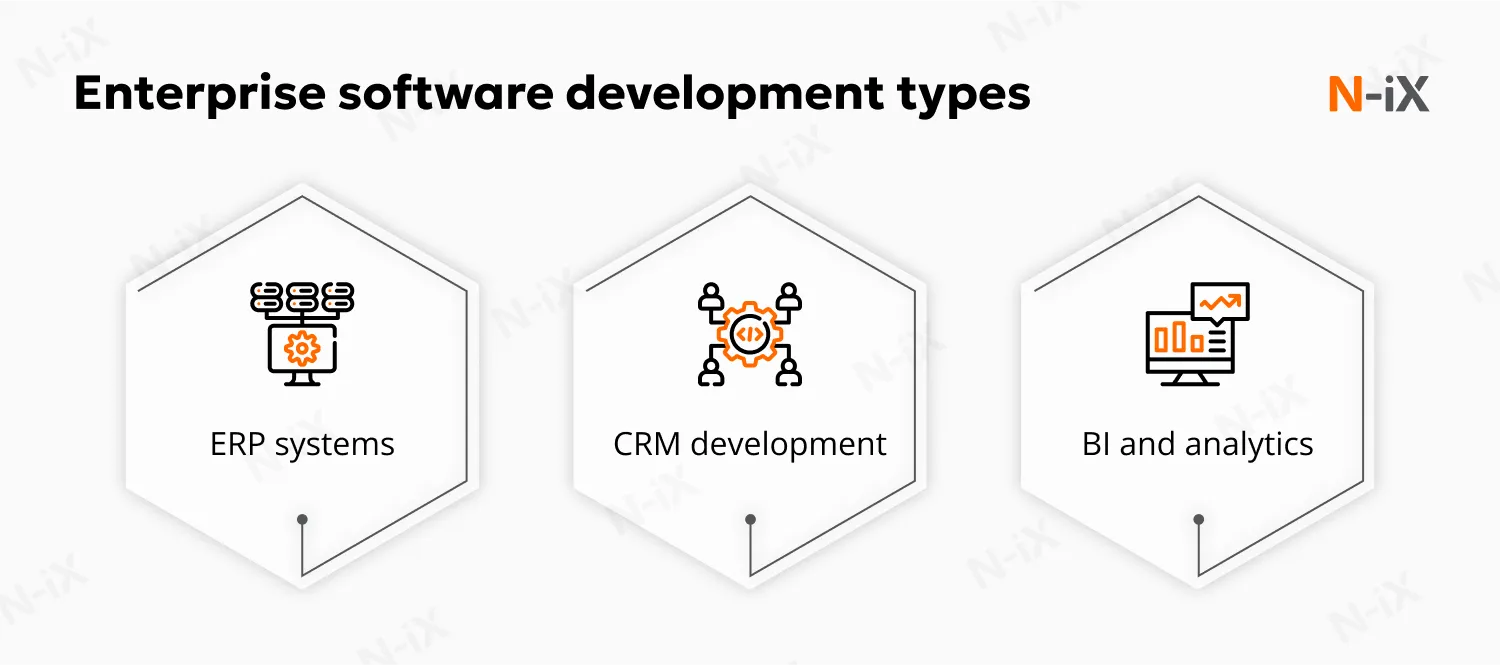
Enterprise software development
Enterprise software development focuses on creating solutions for business organizations, addressing complex workflows, data management, and integration challenges that large organizations face. It includes the following types of software development:
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems
ERP development involves creating comprehensive software solutions that integrate various business processes across an organization. These systems typically handle everything from human resources and accounting to supply chain management and customer relationships.
ERP developers must understand complex business processes, database design, and system integration patterns. They often work with enterprise-grade technologies like SAP, Oracle, or Microsoft Dynamics, requiring knowledge of the technical platforms and the business domains they serve.
The challenge in ERP development lies not just in the technical complexity but in understanding diverse business requirements and creating flexible systems that can adapt to different organizational structures and processes.
Customer relationship management (CRM) development
CRM systems help organizations manage interactions with customers and prospects throughout the sales and service lifecycle. CRM developers create software that tracks customer interactions, manages sales pipelines, and provides analytics to improve business relationships.
Modern CRM development increasingly involves integrating marketing automation platforms, social media channels, and communication tools. Developers must create systems that can handle large volumes of customer data while providing intuitive interfaces for sales and marketing teams.
Businesses implementing CRM solutions benefit from cloud-based platforms that offer scalable architecture and seamless integrations through robust APIs. These multi-tenant systems reduce infrastructure overhead while maintaining data security and customization capabilities for their specific organizational needs.
Business Intelligence (BI) and analytics
BI development focuses on creating systems that help organizations make data-driven decisions. BI developers build data pipelines, create analytical models, and develop visualization tools that transform raw business data into actionable insights.
This field combines software development with data science, requiring skills in database design, data processing frameworks like Apache Spark, and visualization libraries. BI developers often work with large datasets and must understand the technical challenges of data processing and the business context needed to create meaningful reports and dashboards.
BI solutions offer businesses competitive advantages through real-time analytics and Machine Learning capabilities that provide instant insights into market trends and operational performance. These sophisticated systems enable predictive modeling and automated decision-making that help companies anticipate customer needs, optimize operations, and respond proactively to market changes.
Read more: Business intelligence development: why, what, how?
Specialized development areas
Beyond the major categories, several specialized types of software development have emerged to address specific technological challenges and opportunities.
Game development
Game development combines technical programming skills with creative design, creating interactive entertainment experiences across various platforms. Game developers work with specialized engines like Unity or Unreal Engine, requiring knowledge of graphics programming, physics simulation, and user interface design.
The gaming industry spans mobile games, console titles, PC games, and emerging platforms like virtual and augmented reality. Each platform presents unique technical challenges, from optimizing performance on mobile devices to leveraging the latest graphics hardware for high-end gaming experiences.
Game development teams typically include programmers specializing in different areas such as gameplay mechanics, graphics rendering, artificial intelligence, and network programming for multiplayer experiences. The industry also requires developers who understand platform-specific requirements for different gaming consoles and distribution platforms.
You may also be interested in: Business analysis outsourcing: Your path to operational excellence
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning development
AI and ML development have become one of the fastest-growing areas in software development. It focuses on creating systems that can learn, adapt, and make decisions. This field requires an understanding of mathematical concepts, statistical modeling, and specialized frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, or scikit-learn.
Machine learning developers create systems for image recognition, natural language processing, recommendation engines, and predictive analytics. The field spans from research-oriented positions developing new algorithms to engineering roles implementing and scaling AI-augmented development solutions in production environments.
The democratization of AI tools and cloud-based machine learning services has made this field more accessible. However, it still requires strong mathematical foundations and an understanding of data science principles. As AI becomes integrated into more applications, demand for developers who can implement and maintain these systems continues to grow.
Blockchain and cryptocurrency development
Blockchain solutions involve creating decentralized applications and systems that leverage distributed ledger technology. Blockchain developers work on cryptocurrency systems, smart contracts, and decentralized applications (DApps) that run on platforms like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, or newer blockchain networks.
This field requires understanding cryptographic principles, distributed systems, and consensus mechanisms. Smart contract developers use languages like Solidity to create self-executing contracts that run on blockchain networks, while blockchain protocol developers work on the underlying infrastructure that powers these networks.
The blockchain space moves rapidly, with new platforms, protocols, and use cases emerging regularly. Developers in this field must stay current with technological developments while understanding decentralized systems' regulatory and business implications.
Emerging trends and future directions
Software development continues to evolve rapidly, with new technologies and approaches constantly emerging. Several trends are shaping the future of software development across all categories.
Artificial Intelligence is being integrated into development tools, with AI-powered code completion, automated testing, and even code generation becoming more sophisticated. These tools are changing how developers work, potentially making development more efficient while raising questions about the future role of human programmers.
Low-code and no-code platforms democratize software development, allowing non-programmers to create applications using visual interfaces and pre-built components. While these platforms won't replace traditional programming for complex applications, they're expanding the number of people who can participate in software creation. This democratization accelerates digital transformation by enabling faster application development, reducing dependency on scarce technical resources, and allowing domain experts to build solutions that directly address their operational needs.
Edge computing drives new development approaches as processing moves closer to data sources and users. This trend is significant for IoT applications, real-time systems, and applications requiring low latency or offline capabilities.
Quantum computing, while still in early stages, represents a potential paradigm shift that could require entirely new programming approaches and algorithms. As quantum computers become more practical, specialized quantum software development may emerge as a distinct field. Understanding these emerging types of software development helps businesses prepare for future technological opportunities and make informed decisions about their digital transformation strategies.
Choosing the right technology partner for your development needs
Selecting the right development partner requires evaluating proven expertise, industry knowledge, and strategic capabilities that align with your business objectives. The ideal partner should demonstrate extensive experience across multiple sectors, maintain robust security practices, and offer comprehensive support throughout your digital transformation journey. Key criteria for evaluating potential partners are:
Proven track record and scale
Look for partners with substantial project delivery experience, large teams of specialized engineers, and decades of experience guiding enterprises through complex digital transformations. The best partners work with both Fortune 500 companies and innovative startups, demonstrating versatility across different business scales.
Industry-specific expertise
Prioritize partners with deep domain knowledge in your sector, whether fintech, healthcare, automotive, retail, or logistics. They should understand industry-specific regulations, compliance requirements, and market dynamics while offering pre-built frameworks and battle-tested solutions for common industry challenges.
End-to-end strategic guidance
Choose partners who provide comprehensive support from initial strategy through post-launch optimization. Look for technology-agnostic recommendations focused on business outcomes, integration of modern practices like AI/ML and cloud-native architectures, and scalable solutions designed for future growth.
Risk mitigation and transparency
Evaluate partners based on their transparent methodologies with clear milestones, flexible engagement models that adapt to your needs and budget, dedicated project management with regular reporting, and strong intellectual property protection and data security protocols.
Global delivery capabilities
Consider partners offering nearshore and offshore delivery options for cost optimization, cultural alignment, and time zone compatibility for seamless collaboration, English-proficient teams with Western business practices, and established processes for remote and hybrid work environments.
FAQ
1. How do I determine which type of software development my business needs?
Choosing among the various types of software development depends on your business goals, target audience, and operational requirements. Mobile app development is essential to reach customers on mobile devices. Enterprise software development might be the best fit for complex business processes and data management. Web development is likely your priority if you want to establish an online presence or create web-based tools. Consider factors like budget, timeline, scalability requirements, and whether you need integration with existing systems. A thorough business analysis and consultation with experienced developers can help identify the most suitable approach for your needs.
2. How do I ensure a development partner has expertise in the right type of development for a project?
Look for development partners with demonstrable experience in your specific type of project through case studies, portfolios, and client testimonials. Ask about their team's technical certifications, years of experience with relevant technologies, and previous projects in your industry. Request references from similar projects and speak with past clients about their experience. Evaluate their development process, quality assurance practices, and post-launch support offerings. A reliable partner should be able to explain technical concepts clearly, provide realistic timelines and budgets, and demonstrate understanding of your project's technical and business aspects. Expertise across different types of software development ensures your partner can adapt to evolving project requirements and recommend the most suitable approach for your specific business needs.
3. What ongoing support and maintenance should be expected after our software is developed?
Software maintenance typically includes bug fixes, security updates, performance optimization, and compatibility updates as underlying platforms evolve. Most development partners offer maintenance contracts that include monitoring, regular updates, backup management, and technical support. This might involve server maintenance, SSL certificate updates, and framework updates for web applications. Mobile apps require updates for new OS versions and app store compliance. Enterprise software often needs integration maintenance as connected systems change.
4. How can intellectual property be protected and data security ensured during development?
Protecting IP and ensuring security requires developing partners with strong security practices and clear legal agreements. Look for partners who sign comprehensive Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and work agreements that assign IP ownership to your organization. Ensure they follow secure development practices, including code reviews, vulnerability testing, and compliance with relevant standards (GDPR, SOC 2, etc.). Ask about their data handling procedures, access controls, and security certifications. Consider partners who can work on-site or provide dedicated development teams for sensitive projects. Regular security audits and penetration testing should be part of the development process.
5. How to evaluate potential development partners effectively?
Key questions include: What similar projects have you completed in our industry? Can you provide references and case studies? What is your development methodology and project management approach? How do you handle changes in requirements during development? What testing and quality assurance processes do you follow? How do you ensure projects stay within the timeline and budget? What post-launch support do you provide? What security measures do you implement? How do you handle IP protection and confidentiality? Can you scale the team up or down as needed? What technologies and frameworks do you specialize in? How do you communicate progress and handle project updates? Understanding their answers will help you assess whether they fit your needs and working style.
Have a question?
Speak to an expert