With more and more sales moving online, it’s becoming challenging for digital retail stores to tackle privacy and security issues in ecommerce. Data from Statista states that ecommerce sales worldwide amounted to $3.53T in 2019, and by 2022 they are projected to grow to whooping $6.54T. As technology gets smarter and hackers more sophisticated, types of security vulnerabilities in ecommerce become more versatile and complex.
According to the 2019 global online shopping survey by 2Checkout, about 76% of online customers consider data privacy and security as very important factors when deciding where to buy. So what are the top security issues in ecommerce retailers should watch out for? And how can online merchants protect themselves and customers from common ecommerce threats? Let’s find out.

#1 Online payment fraud
Within the recent years, we have all witnessed a shift from physical to online transactions. Today, people don’t need to present a card to merchants at the time when an order is given and payment effected. It seems that the number of credit card fraud should have fallen, because credit card information is not physically disclosed to third-parties. But in fact, credit card incidents have increased to 25% of all incidents. Within ecommerce, CNP (Card Not Present) data incidents are responsible for 84% of all incidents, according to 2019 Trustwave Global Security Report. Payment fraud is one of the most popular types of security vulnerabilities in ecommerce. Moreover, CNP fraud is expected to increase by 14% by 2023 and retailers could lose $13B by that time. There are a lot of different types of online payment fraud, but the most common ones are identity theft, friendly fraud, triangulation, and clean fraud.
It’s no wonder that during high spikes like the holiday season there are higher volumes of attempted online payment fraud. Especially, this is true of friendly fraud.
“Historical data, such as from the 2009 recession, shows that during downturns, fraud usually becomes higher. This means an increase in friendly fraud (such as buying a high-value item online like a large, flat-screen TV, and then claiming that it was a fraudulent transaction). While merchants dispute chargebacks when they can identify friendly fraud, only 32% of them are successful more than 45% of the time when disputing chargebacks.” - Best Practices For ecommerce And Retail Fraud Management, Forrester Research, Inc., July 22, 2020
Also, a surge in online shopping during pandemic lockdowns has spurred the number of online payment fraud. For instance, in the UK, the research shows that 16,352 people fell victim to online shopping fraud. So what can be done about transaction fraud?
How to prevent it:
There are several basic things that online retailers can do to protect themselves and consumers from online payment fraud:
- Achieve and maintain the PCI standard that ensures credit card information collected online is being transmitted and stored securely or choose a reliable PCI compliant payment system provider.
- Use an Address Verification System (AVS) that compares a customer’s billing address against the information stored on file by a credit card issuer.
- Use Secure Server Layer (SSL) certificates that guarantee that all the sensitive communications on your website occur through a secure channel using data encryption.
- Switch to HTTPS protocols that protect customer data and the sensitive information they submit.
- Use mandatory CVV for all ecommerce transactions that are carried out using credit or debit cards.
- Ensure multi-factor authentication and encourage consumers create stronger passwords.
- Make use of AI/ ML algorithms in ecommerce and retail fraud management (ERFM). They can catch anomalies and send a notification if something goes wrong or even cancel a transaction. However, you should ensure that you have great visibility into how exactly AI/ ML algorithms are making decisions for a particular customer-facing process.
“Today’s ERFM solutions provide only minimal insight into and customer tuning of their AI and machine learning (ML) models. This causes significant headaches with retailers who need their investigators to understand why the AI algorithm declined a transaction in order to explain it to both the customer and auditors. The good news is that vendors are putting more emphasis in their roadmaps to: 1) “rely less on black box models” and to 2) build explanation features into their AI/ML models.” - Best Practices For ecommerce And Retail Fraud Management, Forrester Research, Inc., July 22, 2020
#2 Misconfigurations of web applications
ecommerce businesses require different types of web apps to satisfy the needs of their consumers. With the help of web apps, it is easy to create lists of products or services, product/service details, a personal profile, a shopping cart and secure e-payment options. Also, most online shopping traffic comes from mobile. Mobile commerce (or "mcommerce") has seen an average year-on-year increase of 33.8% since 2016. This makes web apps the best choice to drive engagement and revenue.
When it comes to security, however, many online retailers fail to take effective security measures throughout the software development life cycle and overlook the importance of configuring web apps. This causes various types of security vulnerabilities in ecommerce web apps that lead to compromised user accounts, installation of malicious code, lost sales revenue, loss of trust with customers, damaged brand reputation, etc. Here is the list of the most common web application attacks:
- Cross-site scripting (XSS) - a client-side code injection attack
- SQL injection - the placement of malicious code in SQL statements via web page input
- Cookie poisoning - the modification of a cookie to gain unauthorized information about the user
- Remote command execution - execution of arbitrary commands on the host operating system via a vulnerable application
- File-path traversal - a technique that allows an attacker to access arbitrary files on the server
“The case with autoincremented id for an order is also one of common misconfigurations that could help your competitors better understand the number of your sales. You can place an order and receive an email with your order-id, and place an order in a week and receive another order-id and see the difference. This is the way of getting private information about your sales someone could use to their advantage. Basically, to avoid such an issue all you need to do is to use a universally unique identifier (UUID) instead of auto incremented id. This is a simple thing but it can save you from a lot of troubles.” - Serhii Yevtushenko, Senior Software Engineer at N-iX
How to prevent it:
To ensure that website applications are secure against malicious threats, online retailers should consider the following items:
- Choose the right web host for your ecommerce website: you can choose among shared hosting, virtual private server, or dedicated hosting depending on your needs. Also, there are managed hosting when you don’t need to take care of setup, configuration, security, maintenance, support, etc. and unmanaged hosting which is usually cheaper, but you have to do all the server setup and configuration yourself.
- Introduce effective monitoring and alerting: you should configure Web Application Firewall that helps identify malicious requests and respond in a way to prevent any loss. There are two common types of firewalls effective for ecommerce websites: Application Getaways and Proxy Firewalls. Also, you need to make use of Runtime application self-protection (RASP) tools that block potentially malicious activity while an application is in production.
- Make use of penetration testing that presupposes running a series of experiments to identify in a computer system, network or web application security vulnerabilities that an attacker could exploit.
- Never use cookies to store highly sensitive or critical information and always encrypt the information that is stored in the cookies.
- Implement the x-xss-protection security header to prevent XSS attacks.
#3 Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
Denial of service (DDos) attacks are used to crash a web server or online system by overwhelming it with traffic that comes from numerous compromised devices. The first symptoms of DDoS include excessive amount of spam emails, slow access to files, Internet disconnection, etc. Sometimes, it is really difficult to detect these symptoms without professional tools and detailed diagnosis.
How to prevent it:
The main thing is to differentiate legitimate spikes in network traffic from fake traffic and block “bad” traffic before it even reaches the site. There several things you can do to prevent and mitigate DDos attacks:
- Leverage a DDoS mitigation solution that filters traffic and blocks DDoS attacks before they can take effect.
- Configure your firewall and router to drop incoming ICMP packets or block DNS responses from outside your network.
- Move to a cloud-based provider that can offer high bandwidth and multiple points-of-presence in data centers around the world.
- Set up a load balancer that will improve network, server, and app performance by distributing traffic caused by malicious activity between several data centers.
#4 Bad bots
Bad bots behave like real users and can be used not only by hackers to steal credit card numbers, CVVs, and log-in credentials of your users, but also by your competitors to manipulate prices of your products, block shopping carts, and create an artificial traffic spike to slow down your ecommerce website.
How to prevent it:
If you want to protect yourself against attacks from bots, there are some effective steps you can take today to start addressing the issue:
- Always evaluate traffic sources
- Investigate sudden traffic spikes
- Monitor for failed login attempts
- Protect exposed APIs and mobile apps
- Use web application firewalls and content delivery network
- Introduce a CAPTCHA test
- Consider investing in a bot mitigation solution
#5 Customer journey hijacking
This type of security threat presupposes injection of unauthorized advertisements into the browsers of visitors to your website in the form of pop-up ads, banners or video ads. Such advertisements not only distract customers on their purchasing journey, but also pose security risk to visitors as they are often powered by malware.
How to prevent it:
Customer journey hijacking is among top concerns for ecommerce businesses as there is little they can do to protect their consumers from this kind of security threat. This is because it is a consumer-side infection rather than a server-side infection. But still online retailers can at least educate users about this issue, encourage them to install antivirus software, antimalware software, and use a virtual private network. Also, they can implement client-side protection. This will allow them to see all unauthorized ads and third parties that are running on your website and block any unauthorized advertising injected into visitor sessions.
#6 E-skimming
This is one of the most dangerous types of security issues in ecommerce also known as ‘Magecart’ attack. Hackers inject the malicious code into payment card processing pages of the website and it captures credit card data as the end user enters it in real time. There are several ways of how hackers gain access to ecommerce websites: via a successful phishing attempt, cross-site scripting, or third-party compromise. As a result, the collected credit card information is either sold or used to make fraudulent purchases.
How to prevent it:
Here are simple things you should know to prevent an e-skimming attack:
- Use antivirus and anti-malware software
- Implement multi-factor authentication
- Create strong, unique passwords on all systems
- Don’t click on suspicious links
- Update and patch all systems with the latest security software
- Configure firewall
- Educate employees about safe cyber practices
- Regularly check JavaScript code on company and partner web pages to detect edits
- Monitor and analyze Web Logs to look for unknown domains
What should online retailers focus on to avoid common types of security vulnerabilities in ecommerce?
An ecommerce website is a complex system consisting of many parts including: a catalog of products, a shopping basket system, online payment systems, personalized profile pages, contact us page, and many more. And there’s a wide range of attack vectors targeted at each of these parts. To get unauthorized information about users, hackers usually look for vulnerabilities in your server, infrastructure, network environment, databases, APIs, integrations with third-party vendors, etc. To ensure your ecommerce site is well defended against cyber-criminals, you should implement security into every step of your website development.
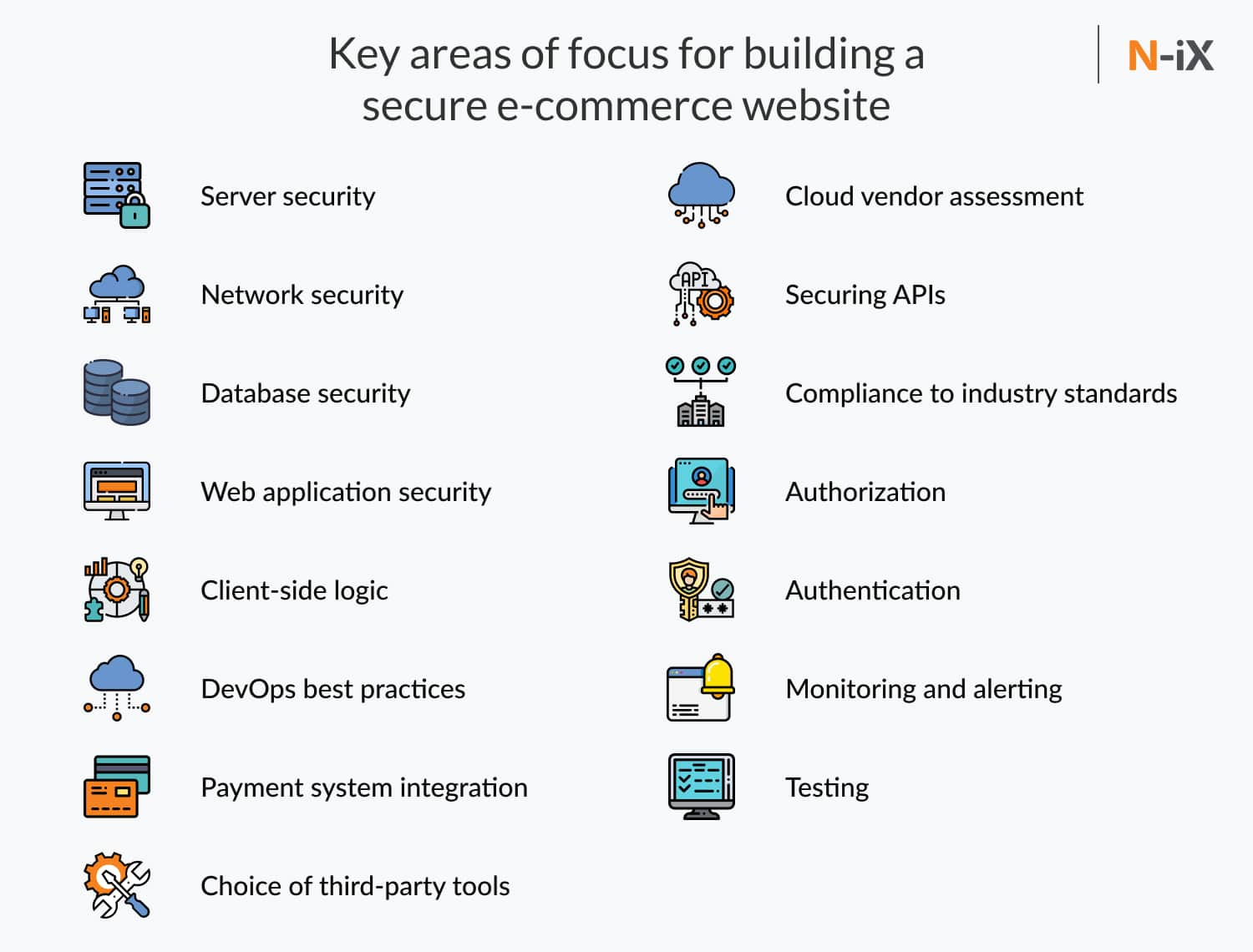
Summing up
The ecommerce industry is increasing year by year so is the scale of attacks on ecommerce businesses. In the rush to satisfy the sudden increase in online shopping, many online retailers have undertaken the ad hoc manner to online store development. As a result, some of them may have overlooked critical types of security vulnerabilities in their ecommerce websites. There is a sheer possibility that your site is being attacked by hackers right now. So it’s high time ecommerce businesses took security risks seriously and started investing in protecting their websites. If you need help with addressing privacy and security issues in your ecommerce website, contact our experts, and they will advise you on the solution.



