The Internet of Robotic Things (IoRT) is opening new doors in automation. It connects robots to the Internet, enabling them to collect, process, and share data autonomously. For businesses in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics, this means more than just smarter robots-it's about improving how things get done: remotely, faster, and more efficiently. It makes these businesses seek expert robotics consulting from tech vendors that can also provide IoT development services and have experience with creating solutions for sensor data processing.
As the world continues to embrace Industry 4.0, the Internet of Robotic Things plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of automation across various sectors. In this article, we'll break down how IoRT is already making a difference and why it's worth paying attention to if you're looking to stay competitive in an increasingly automated world.
What is the Internet of Robotic Things (IoRT)?
The Internet of Robotic Things (IoRT) combines robotics with the Internet of Things (IoT). This convergence enables robots to not only perform pre-programmed tasks but also to adapt to their environment by gathering and processing data in real time. As a result, robots can act on the information they receive, communicate with other devices, and even make autonomous decisions without human intervention.
How IoRT fits into your architecture
IoRT solutions typically combine robots, IoT sensors, connectivity layers, and edge or cloud platforms into one coordinated system. Robots collect data through onboard and external sensors, process it locally on edge devices for real-time decisions, and send enriched data to the cloud for long-term analytics. Gateways ensure secure communication between robots, shopfloor equipment, and enterprise systems such as MES, WMS, or ERP.
Key technologies powering IoRT
The new manufacturing approaches enabled by IoRT are already incentivising the growth of this tech market. According to the Research and Markets report, the IoRT market size is expected to grow from $34.36B in 2025 to $162.02B in 2030 [1]. This fivefold increase is no wonder. While robotics and IoT are paramount to the success of IoRT solutions, they are often paired with other technologies that are developed quickly. Together, they enable the creation of autonomous and intelligent robots. Let's review them.

IoT sensors
They allow robots to monitor their surroundings, collect real-time data, and interact with other devices. This data is essential for driving decision-making, improving performance, and ensuring task efficiency.
For a deeper dive into the integration of sensors with robotics, check out how sensor fusion in robotics drives intelligent automation
Edge AI
Edge computing enables on-device AI, bringing computational power and real-time data processing and decision-making at the edge of the network. This reduces latency and ensures that robots can make critical decisions without depending on distant cloud servers.
More on topic: AI in robotics: 15 use cases, implementation process, and best practices
Harness AIoT for smarter operations—get the guide to industry use cases!


Success!

Cloud computing
Cloud platforms play a significant role in managing the vast amounts of data generated by IoRT systems. By storing and analyzing data in the cloud, robots can interact with advanced AI models, thereby improving their performance across tasks and locations.
Computer vision (CV)
Computer vision allows robots to "see" and understand their environment through cameras and visual data. By using advanced image recognition algorithms, robots can detect objects, navigate environments, and even identify product defects. In manufacturing, for example, CV enables robots to inspect assembly lines and ensure that products meet quality standards, reducing human error and improving consistency.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
When combined with IoRT, RPA enables robots to execute both physical and digital tasks in a unified way, enhancing productivity and reducing manual errors. For example, in logistics, robots can autonomously move goods while also updating inventory management systems in real-time.
5G connectivity
With 5G, robots can transmit large amounts of data faster, enabling quick responses and continuous communication across various devices in the system. This is essential for environments that require instant data transfer, such as autonomous vehicles or industrial robotics operating in real time across multiple machines.
The mentioned technologies enable faster data transfer, real-time decision-making, and increased automation. Let's explore other benefits businesses can gain from IoRT.
What benefits can businesses achieve with IoRT adoption?
Adopting the Internet of Robotic Things allows businesses to improve operations on shop floors, in warehouses, and in between. Let's explore how in more detail.
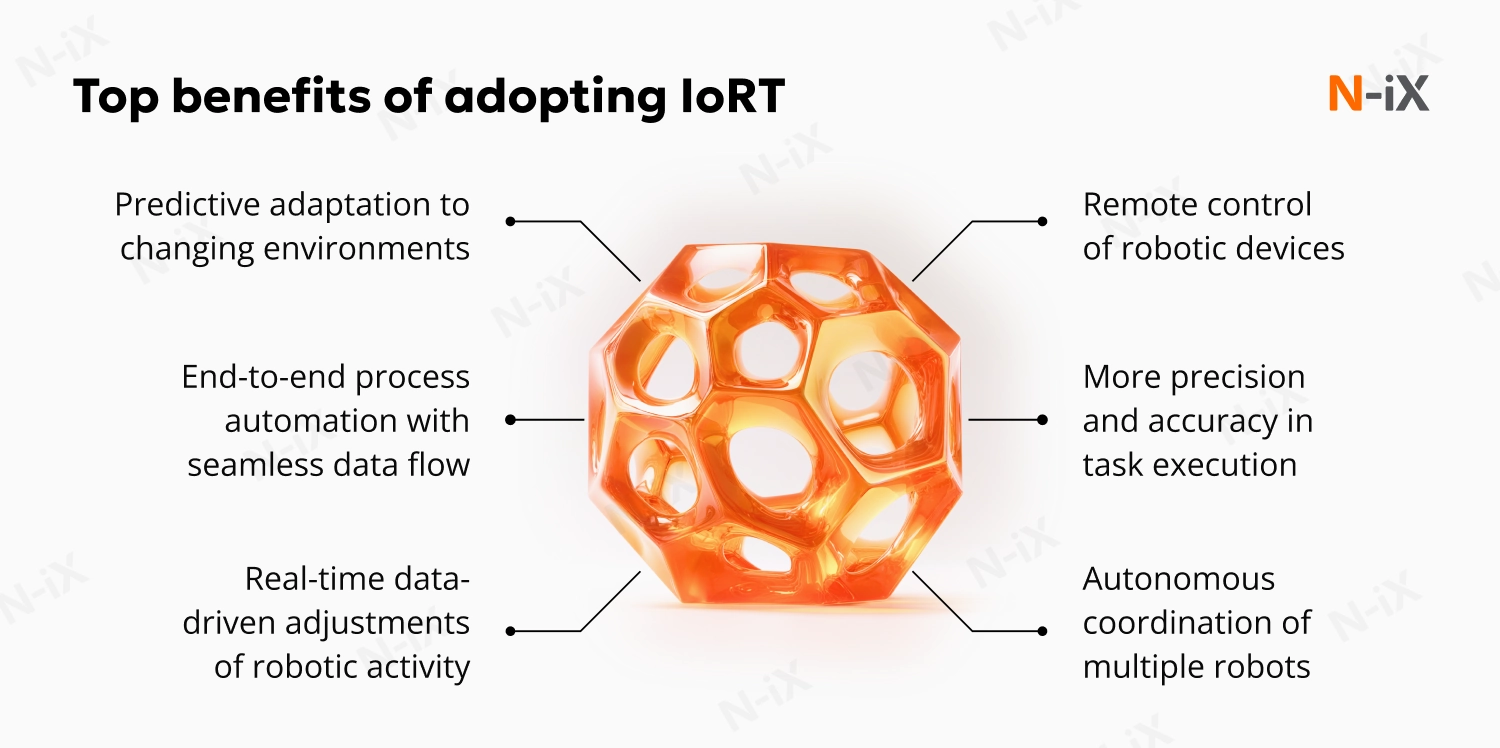
Remote control of robotic devices
The Internet of Robotic Things enables robots to be remotely controlled and monitored in environments that are dangerous, hazardous, or difficult for humans to access. For instance, in mining operations, IoRT-powered robots can perform real-time inspections, monitor equipment conditions, or carry out maintenance tasks deep underground. These robots send live data to operators, allowing them to make informed decisions without putting human workers at risk.
More precision and accuracy in task execution
With IoRT, robots can be connected to IoT systems, enabling them to monitor and adjust their actions in real time continuously. For example, in a manufacturing facility, IoRT-enabled robots can track and respond to sensor data, ensuring parts are produced with high precision and accuracy. This capability allows manufacturers to create more complex products with better quality and fewer defects.
Autonomous coordination of multiple robots
With IoRT, businesses can have robots working in tandem without human intervention. For instance, in a large warehouse, multiple robots equipped with IoT sensors can communicate with one another to efficiently pick and sort items, ensuring smooth, coordinated operations. This level of autonomous coordination can only be achieved when robots are connected via IoT.
Real-time data-driven adjustments of robotic activity
IoRT enables robots to adjust their actions in real time based on data. In precision manufacturing, robots can continuously monitor environmental factors, such as temperature and material quality, and adapt their processes accordingly. This constant feedback loop, powered by IoT, enables robots to optimize their performance on the fly, something traditional automation cannot do.
End-to-end process automation with seamless data flow
With IoRT, robots not only perform tasks but also share data across systems, creating an integrated workflow. For instance, in an assembly line, robots can detect production issues, communicate with other machines, and autonomously adjust the workflow or flag issues to workers in high-risk, high-value manufacturing environments.
Predictive adaptation to changing environments
IoRT robots can adapt to changing environments in real time by processing data from their sensors and connected systems. In agriculture, for example, robots equipped with IoT sensors can detect changes in soil conditions or crop health and adjust their tasks, like watering or harvesting, accordingly. This ensures optimal efficiency throughout the growing season.
These benefits of IoRT can be attractive to many businesses that use robotics. Here are a few applications of the Internet of Robotic Things across various domains.
Applications of IoRT across industries
Businesses consider adopting the Internet of Robotic Things to optimize and automate their processes and eliminate as many human employees as possible. While some do so from an economic perspective (i.e., robots can work longer shifts, producing more services/products), other businesses may use robotics to eliminate human labor in hazardous conditions. Below, we've collected the most common Internet of Robotic Things applications across various industries.
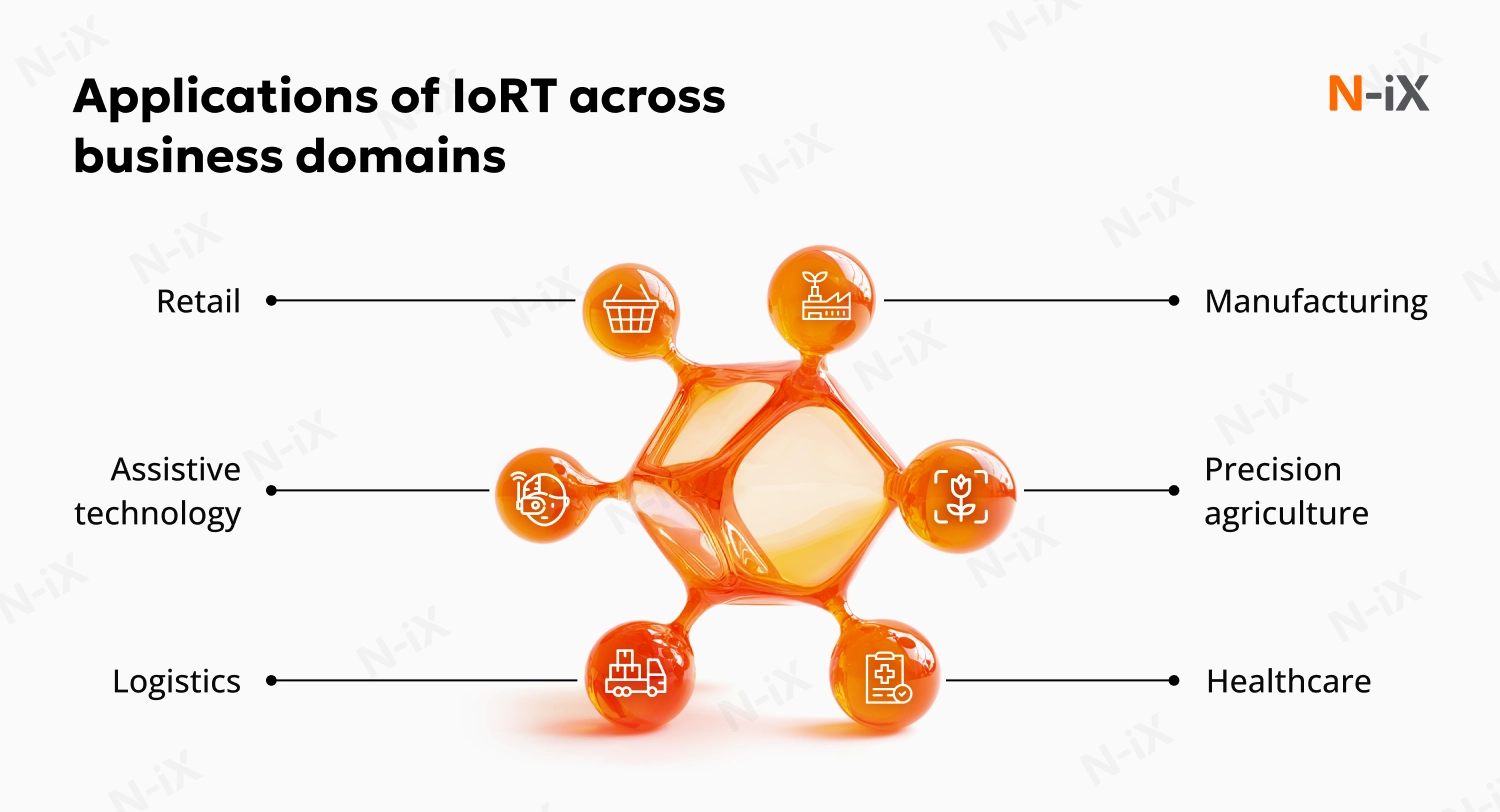
Manufacturing
One of the most significant applications of IoRT is in manufacturing. Robots can be equipped with IoT sensors to monitor assembly lines, track production status, and provide data to optimize workflows. IoRT-powered robots can predict equipment failure, manage inventory, and automate complex tasks, boosting production efficiency, and decreasing downtime.
Explore top 8 ways how IoT devices decrease downtime in a manufacturing plant
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, IoRT is revolutionizing patient care and operational efficiency. Robots can autonomously monitor patients, deliver medications, and assist in surgeries, improving patient outcomes and reducing human error. IoRT's real-time data transmission ensures doctors and healthcare professionals receive the most up-to-date information to make informed decisions.
Logistics
IoRT plays a crucial role in the logistics industry, where robots are used for autonomous delivery, real-time inventory management, and smart warehousing. IoRT-equipped robots can navigate warehouses, communicate with inventory management systems, and optimize delivery routes, leading to faster and more efficient operations.
As stated in the McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook 2025 report, warehouse businesses are already using autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) to transport materials within the vicinity [2]. However, for safety reasons, their area of activity is often separated from that of human workers. The trend is to design and deploy cobots (collaborative robots that assist humans) that can expand the range of tasks and operate safely alongside humans. This can be achieved through technologies such as IoT, computer vision, edge AI, and others.
Retail
Retailers use IoRT to streamline operations, including stock monitoring, automated checkout, and customer service. Robots collecting real-time data on consumer behavior, product stock levels, and other factors that influence purchasing decisions can be one of many Internet of Robotic Things examples used in retail.
Assistive technology
Researchers like Moid Sandhu et al., in their "Internet of robotic things for independent living" article, mention that IoRT can significantly enhance independent living by providing real-time assistance with daily activities such as meal preparation, mobility support, and cleaning [3]. Embedded sensors in wearable devices or robots continuously monitor health parameters, triggering immediate alerts or emergency assistance if needed. Additionally, IoRT-powered robots can combat loneliness by facilitating social interactions and offering companionship, improving both physical and emotional well-being for individuals living alone.
Precision agriculture
IoRT in precision agriculture enables robots to autonomously collect and process data from the field in real-time. Drones equipped with IoT sensors scan crops, while ground robots perform tasks like targeted pesticide spraying and automated irrigation. This seamless data flow ensures efficient resource usage and higher crop yields. IoRT helps farmers monitor and manage crops with greater accuracy, improving sustainability and reducing operational costs.
While many industries may benefit from the Internet of Robotic Things, they'll do so only if its adoption and integration into the tech ecosystem are executed properly. Let's review a few challenges that may arise along the way so you can develop strategies to address them from the start.
Challenges in implementing the Internet of Robotic Things
- Security. The connectivity that makes IoRT possible also exposes systems to cyber threats. Hackers could access sensitive data or take control of robotic systems, posing significant security risks.
- Scalability. Scaling IoRT solutions across large organizations can be complex. As systems expand, maintaining communication between robots, sensors, and other connected devices becomes challenging.
- Integration. Most industrial environments rely on established PLCs, SCADA, and MES platforms. Adding IoRT requires bridging OT and IT systems through standardized protocols such as OPC UA, MQTT, or industrial Ethernet.
The good news is that these challenges are manageable. For example, implementing robust security measures, such as end-to-end encryption and access control, helps secure IoRT systems. Scalability is ensured through effective infrastructure planning, and smooth integration is achieved through seamless communication between devices and existing platforms. The thing is, each of these and other steps requires careful planning and often custom solution development. This is where an experienced software development company like N-iX can become a reliable tech partner.
How N-iX can help
At N-iX, we specialize in building end-to-end IoRT solutions tailored to your business needs. Our expertise in robotics, AI, IoT, cloud, AR/VR, IoT connectivity, and other technologies allows us to integrate intelligent robots into your operations, optimizing efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing decision-making.
We have over 23 years of experience in developing custom software for various industries. N-iX helps businesses from finance, manufacturing, logistics and supply chain, retail, telecom, automotive, healthcare, energy and utilities, and agritech build reliable solutions to improve business performance.
N-iX also holds several partnerships with tech companies that provide hardware and software components necessary for the IoRT solutions. They include Arduino, Raspberry Pi, MATLAB, and Nordic Semiconductor. Moreover, we are certified partners of GCP, Microsoft Azure, and AWS cloud solutions and services, which are often used for IoRT data processing.
Final thoughts
The Internet of Robotic Things (IoRT) is transforming industries by merging IoT with robotics to create smarter, more efficient operations. While there are challenges to overcome, the benefits of IoRT are undeniable, including improved efficiency, autonomy, and scalability. As we look to the future, IoRT will continue to evolve, driving advancements in manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and other industries.
To stay ahead, organizations embrace IoRT technologies for enhanced automation and better decision-making. N-iX offers extensive services to help your business build and adopt IoRT and enter the era of Industry 4.0. Let's discuss where our tech expertise can support your business vision.
Sources:
- Internet of Robotic Things Market - Forecasts from 2025 to 2030 | Research and Markets
- McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook 2025 | McKinsey
- Internet of robotic things for independent living: Critical analysis and future directions. Moid Sandhu et al., Internet of Things, Volume 25, 2024.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between IoT and IoRT?
While both IoT (Internet of Things) and IoRT (Internet of Robotic Things) involve connecting devices to the internet for data exchange, the key difference is the autonomy and decision-making capabilities in IoRT. IoT focuses on sensors and devices exchanging data, whereas IoRT integrates robotic systems that not only collect data but also act on it autonomously. This means IoRT robots can perform tasks without human intervention, adapting to their environment and making real-time decisions.
2. What is IoT in robotics?
IoT in robotics refers to the use of internet-connected sensors and devices within robotic systems. These sensors collect data from the robot's environment, such as temperature, movement, and pressure, and send it to a cloud or local system for analysis. This data helps robots make informed decisions, adapt to changing conditions, and improve task performance. Essentially, IoT enables robots to be more intelligent, connected, and autonomous.
3. How does IoRT improve industrial automation?
IoRT significantly enhances industrial automation by enabling robots to not only collect data from their environment but also act on it in real-time. For example, IoRT-powered robots can autonomously monitor production lines, adjust operations based on real-time data, and collaborate seamlessly with other robots. This leads to improved efficiency, precision, reduced human error, and higher production speeds. Additionally, IoRT robots can perform tasks in dangerous environments, minimizing human exposure to risks.
4. Can the Internet of Robotic Things be integrated into existing manufacturing systems?
Yes, IoRT can be integrated into existing manufacturing systems, but it requires careful planning. The integration involves ensuring that the IoRT robots and sensors can communicate seamlessly with your existing PLC, SCADA, and ERP systems. IoRT solutions typically rely on standardized communication protocols, such as OPC UA or MQTT to bridge the gap between old and new technologies. A gradual approach with pilot projects is recommended to ensure compatibility and minimize disruptions.
Have a question?
Speak to an expert