Imagine a bank wants to improve its fraud detection system. Modern fraud patterns evolve quickly, so the bank needs AI models that can recognize unusual transactions and spot anomalies. That requires access to thousands of customer transactions, account activity, and other sensitive data.
However, real data is often difficult to access, expensive to use, and highly regulated. For executives, this creates bottlenecks: rising compliance risks and limited scalability for AI initiatives.
Synthetic data generation offers a powerful alternative. By simulating realistic transaction data without exposing actual customer information, organizations can build and test AI models faster, reduce legal risks, and improve operational efficiency.
To make the most of synthetic data, companies often rely on data analytics expertise to ensure the datasets are accurate, representative, and ready for AI-driven insights. Properly modeled synthetic data can feed machine learning pipelines, enabling smarter decision-making and driving AI innovation forward.
What is synthetic data?
Synthetic data is artificially generated information that mimics real-world data, but doesn't expose real people, events, or sensitive information. Instead, synthetic data preserves the underlying structure, patterns, and statistical relationships of the original dataset, ensuring that models trained on it are as effective as those trained on real data.
Generated through AI algorithms, ML models, and simulations, synthetic data can take many forms, including text, tables, images, and numerical data. These algorithms replace personally identifiable information (PII) with anonymized, synthetic data while retaining the core patterns of the original data.
One of the most crucial and widely applied use cases of synthetic data is in training AI models. It allows organizations to generate large volumes of labeled data without privacy concerns or the limitations of real data collection. This is especially valuable in industries like healthcare and finance, where real-world data may be scarce or subject to strict regulations.
Ultimately, the goal of generating synthetic data is to provide stakeholders with fast access to privacy-preserving, fictional yet functional datasets that capture the complexities of the original individual-level data.
In fraud detection, the bank can generate realistic transaction datasets that reflect real-world patterns, including rare fraudulent behaviors. This allows them to train more accurate AI models, test systems, and simulate financial scenarios safely and efficiently, all while staying compliant and reducing legal risk.
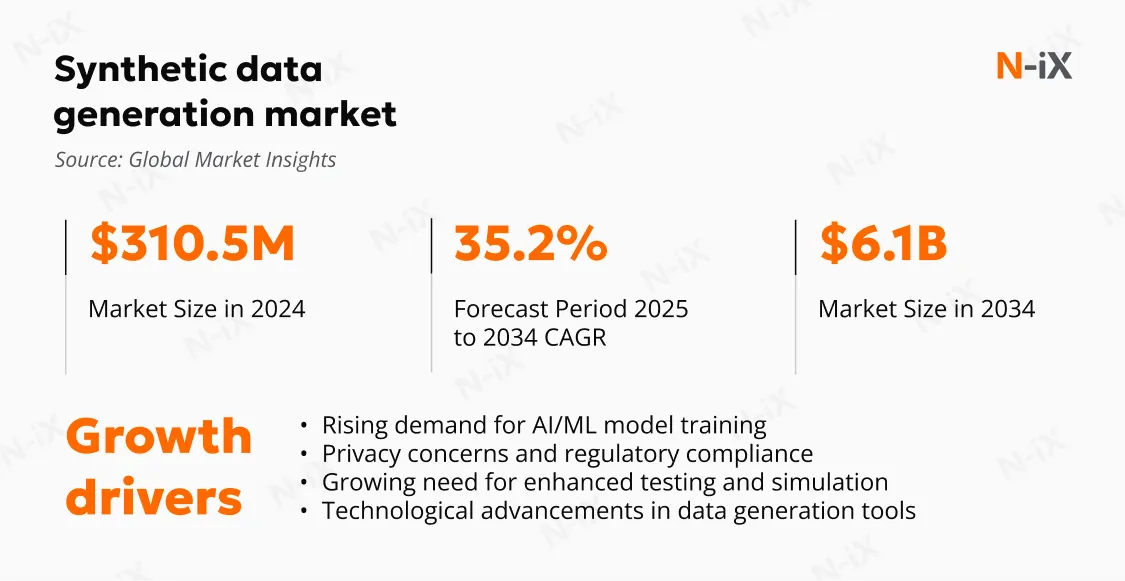
Synthetic data vs real data: A side-by-side comparison
|
Aspect |
Synthetic data |
Real data |
|
Definition |
Artificially generated data that mimics real-world patterns without exposing personal information. |
Data collected directly from real users, behaviors, and events. |
|
Source |
Created using algorithms, simulations, or AI models. |
Gathered from transactions, interactions, surveys, sensors, etc. |
|
Data privacy |
High. No sensitive or identifiable information involved. |
Variable. Often contains personal data that requires strict protection. |
|
Accuracy |
Approximates real patterns; ideal for testing and modeling. |
Highly accurate reflection of real events and conditions. |
|
Data utility |
Excellent for development, testing, scaling, and experimentation. |
Essential for making informed decisions and ensuring regulatory compliance |
|
Cost of acquisition |
Low. Generated programmatically at scale. |
High. Requires collection pipelines, cleaning, and governance. |
|
Bias control |
It can be designed to reduce bias depending on the input model. |
Often contains baked-in real-world bias from processes and sampling. |
|
Scalability |
Unlimited. Can generate as much as needed, instantly. |
Limited by availability, regulations, and collection methods. |
|
Use cases |
Prototyping, algorithm development, simulations, privacy-preserving analytics. |
Production-grade analytics, regulatory reporting, real customer insights. |
Why use synthetic data?
Companies rely on synthetic data for AI model training, QA, data augmentation, financial modeling, and healthcare research, where large datasets are required. Still, they may be sensitive or restricted by privacy regulations. Here are some of the reasons to use synthetic data:
Solve data scarcity
- Some events (e.g., a market crash or a medical anomaly) rarely occur in real datasets. Synthetic data generation simulates rare scenarios at scale and trains models to recognize them.
- Real-world data often leans heavily toward one class. Synthetic data lets you strengthen underrepresented groups, leading to more accurate models.
- When data collection is slow, expensive, or limited, you can add synthetic data to get the needed volume.
Minimizing legal and privacy risks
- Because the data doesn't correspond to real individuals, companies stay safer under GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy regulations.
- Eliminating real personal data from workflows reduces the risk of costly legal actions.
Cost efficiency
- Generating synthetic data helps you avoid the expense of surveys, manual labeling, or specialized data-gathering processes.
- Synthetic data can be created on demand, so you don't need to maintain massive historical datasets.
- With fewer privacy risks, organizations can reduce compliance spend on legal reviews, audits, and regulatory safeguards.
A new must-have for AI model training
- Synthetic data enables the creation of large, diverse, and accurate datasets that are essential for training robust AI models.
- Synthetic data empowers companies to simulate rare events, enhance underrepresented data, and explore new possibilities, driving innovation in AI.
- Whether addressing data scarcity, improving model accuracy, or enabling new AI applications, synthetic data is now a critical resource for developing cutting-edge AI systems.
Top synthetic data use cases across industries
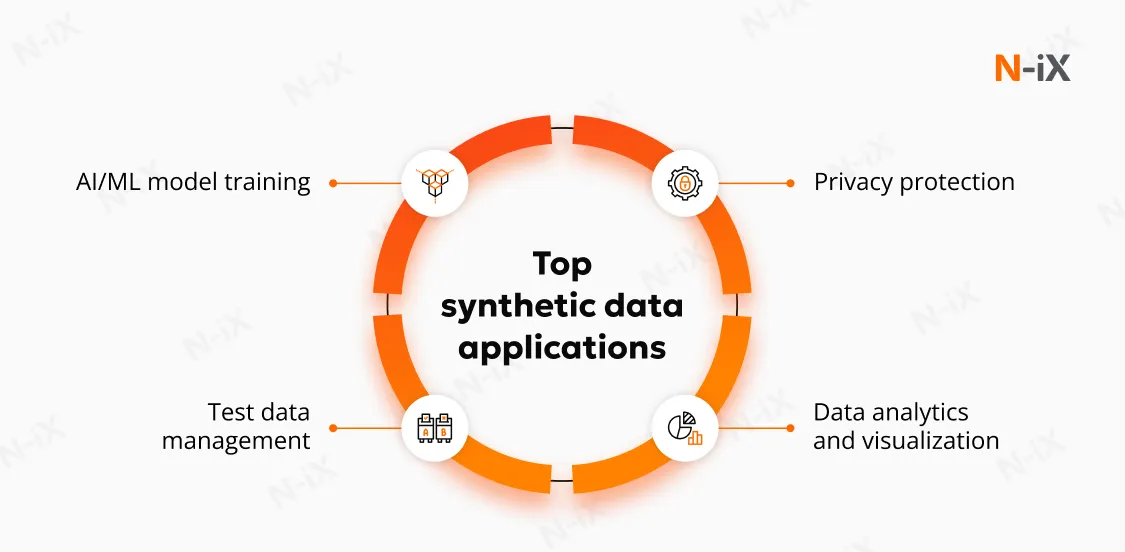
General use cases
Synthetic data supports secure collaboration, compliance, and experimentation across departments and external partners:
- Data sharing with third parties: Collaborations with fintechs, medtechs, or supply chain partners often require sensitive information. Synthetic data allows you to share datasets for vendor evaluation, testing, and joint development without exposing confidential data.
- Internal data sharing: Privacy regulations can hinder cross-departmental data sharing. Synthetic datasets enable teams to collaborate freely, accelerating innovation and experimentation.
- Cloud migration: using synthetic data, you can leverage cloud services for AI and analytics pipelines while protecting private information.
- Data retention compliance: synthetic data preserves historical patterns for trend analysis, seasonal studies, or anomaly detection without storing identifiable records, helping you stay compliant with data retention laws.
Healthcare
Synthetic data in healthcare enables testing diagnostics, training algorithms, simulating treatments, and analyzing population health trends without using patient information. This supports personalized medicine, improves predictive modeling, and enables secure collaboration across institutions while remaining fully compliant with regulations such as HIPAA. Moreover, because artificial data are not specific to real patients, the institutional review board (IRB) or ethics committee approval process is streamlined, significantly reducing time-to-insight.
Financial services
In finance, synthetic data supports secure model development for fraud detection, risk assessment, and analytics without exposing real client data. Organizations like JPMorgan use synthetic data sandboxes to simulate realistic financial scenarios, including transaction patterns, account activity, and rare events such as market crashes or complex fraud. It also improves model accuracy and speeds up development.
Retail analytics
Synthetic data generation helps retailers analyze customer behavior, shopping habits, and seasonal demand while protecting privacy. For instance, Walmart uses it to simulate purchasing patterns, optimize inventory, forecast demand, and test new products or pricing strategies, predicting customer responses without relying on real customer data.
Read more about retail data monetization: why it's worth it and how to do it effectively
Manufacturing
Auto manufacturers use synthetic data to recreate thousands of driving scenarios for autonomous vehicles. This allows them to train ML models to recognize and react to diverse road conditions without relying solely on real-world testing. This not only accelerates testing but also ensures vehicles are safer and more reliable.
Synthetic data generation: Methods and tools
Synthetic data generation methods
There are multiple approaches to generating synthetic data, each suited to different data types, levels of complexity, and business goals. Here's a breakdown of the most commonly used synthetic data generation methods:
Random data generation
This method can generate synthetic data points using random values within defined ranges or formats.
- Best for: Basic testing, demos, placeholder data
- Business value: Quick and inexpensive for low-risk use cases
- Limitation: No correlation to real-world patterns, not suitable for AI or analytics
Rule-based generation
Data is generated using predefined logic or business rules that reflect how real systems behave under known conditions.
- Best for: Simulating structured records, system behavior, or known workflows
- Business value: Full control over the data structure; reliable for testing and validation
- Limitation: Limited realism and variability; lacks the nuance needed for machine learning
Simulation-based generation
This approach models real-world processes or systems using mathematical or physical simulations, for example, how customers interact with a platform or how vehicles behave in traffic.
- Best for: Testing rare events, stress testing, dynamic environments (e.g., logistics, finance, autonomous vehicles)
- Business value: Can recreate edge cases that rarely appear in historical data
- Limitation: Requires domain expertise and accurate modeling of system dynamics
Generative models
These statistical models learn from real data and recreate similar distributions and dependencies.
- Best for: Structured datasets where preserving relationships is critical
- Business value: Balances realism with privacy; ideal for data augmentation and analytics
- Limitation: Performance depends on the quality and completeness of source data
Deep learning methods
Advanced neural networks such as GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) or VAEs (Variational Autoencoders) can generate highly realistic, high-dimensional synthetic data, including images, speech, and behavior patterns.
- Best for: AI model training, media synthesis, customer behavior modeling
- Business value: High realism and scalability for cutting-edge AI initiatives
- Limitation: Complex to develop and tune; requires significant data science expertise
Choosing the right method depends not just on data but on what you want to achieve with it. That's why at N-iX we tailor synthetic data strategies to each organization's technical and business needs, ensuring every dataset is fit for purpose, compliant, and scalable.
Synthetic data generation tools
To select the right tool, we consider factors like data accuracy, scalability, computational requirements, and integration effort. It's often best to start small, generate a limited dataset, validate the output, and refine the setup before scaling to production. Both open-source and commercial platforms offer a range of methods, from rule-based generation to advanced AI models. A few notable examples include:
- CTGAN: A GAN‑based model explicitly designed to generate synthetic data for high‑fidelity tabular datasets, particularly when datasets contain complex relationships and minority classes.
- DoppelGANger: A generative model tailored for time‑series data, commonly used in finance, IoT, and network analytics to replicate sequential patterns and rare events.
- Synner: A user‑friendly synthetic data generator that helps teams create large, diverse datasets without deep technical expertise, supporting multiple formats and business scenarios.
- Synthea: An open-source platform for producing realistic synthetic healthcare records, including patient histories, clinical events, and demographics-widely used for testing and research.
- SDV (Synthetic Data Vault): A comprehensive framework that supports multiple models (GANs, VAEs, copulas) for generating realistic structured data across industries.
- TGAN: A GAN-based tool optimized for high-dimensional tabular data, preserving statistical properties and feature interactions for AI training and simulation.
- MirrorDataGenerator: A privacy-focused generator that produces synthetic datasets mirroring the statistical patterns of sensitive data while minimizing re‑identification risk.
- Plaitpy: A Python library for creating realistic synthetic datasets for software testing and machine learning, replicating real-world distributions and correlations.
- SmartNoise: A differential privacy-driven framework from OpenDP that enables secure synthetic data generation and safe data sharing while meeting regulatory compliance.
At N-iX, we help enterprises evaluate, integrate, or build synthetic data tools that match their technical and compliance needs, ensuring data generation workflows are scalable, secure, and effective.
Challenges of synthetic data generation
While synthetic data offers clear advantages, implementing it effectively comes with several challenges that organizations must consider.
Expertise and technical complexity
- Generating high-quality synthetic data requires skilled data scientists with deep experience in data modeling.
- Choosing the right algorithms (GANs, VAEs, rule-based methods, etc.) and ensuring the synthetic data accurately reflects complex real-world patterns is technically demanding.
- There is often a trade-off between realism and computational feasibility, meaning generating truly accurate datasets can be resource-intensive.
How N-iX helps: We bring deep expertise in data science and AI to select and implement the best algorithms, ensuring high-quality, realistic data that integrates smoothly with your systems.
Understanding real data
- Creating realistic synthetic data starts with a deep understanding of the original dataset and its environment.
- Real-world data often contains subtle, intricate patterns that are difficult to replicate, especially for large, unstructured, or diverse datasets.
- If the base data contains biases or flaws, these may carry over into the synthetic data, potentially amplifying problems downstream.
How N-iX helps: We work closely with clients to understand their data environment and its specific challenges. Leveraging our experience with diverse datasets and industries, we ensure that synthetic data closely mirrors real-world behaviors and accurately reflects the underlying data structures. We also apply sophisticated data validation techniques to identify and mitigate any biases or flaws that might carry over into the synthetic dataset.
Data quality and relevance
- Synthetic data may struggle with accuracy and realism, leading to models that perform well in testing but poorly in production.
- Validating synthetic data is critical: organizations must ensure that it preserves key statistical properties and relationships of the original data.
- As real-world conditions change, synthetic datasets can become outdated, requiring ongoing updates to remain relevant.
- Rare but important edge cases may be underrepresented or missed, reducing utility in critical scenarios.
How N-iX helps: We ensure continuous updates and validation of synthetic datasets, keeping them relevant and reflective of current real-world conditions. Our validation processes ensure the data remains accurate and that model performance is maintained as the environment changes.
Ethical and privacy considerations
- Synthetic data can inherit biases from the original dataset, including selection bias, algorithmic bias, or reinforcement of societal prejudices.
- Organizations should implement strong governance frameworks to ensure transparency, accountability, and ethical use.
How N-iX helps: We implement robust governance frameworks to ensure ethical synthetic data creation, with a focus on mitigating bias. Our solutions comply with all relevant data protection regulations, ensuring privacy, transparency, and security throughout the process.
Explore more about data governance for AI
The future of synthetic data
Synthetic data is quickly shifting from an experimental concept to a strategic enabler of enterprise AI. As technologies advance, they are playing a central role in helping businesses balance innovation with data privacy, compliance, and operational efficiency. Key trends shaping the future of synthetic data:
- Generative AI techniques: Advances in models such as GANs and VAEs are making synthetic data more realistic and statistically accurate. These technologies help organizations simulate rare events, fill data gaps, and improve model performance while maintaining privacy.
- On-demand generation: Real-time, automated synthetic data generation is becoming a reality. Enterprises will soon be able to generate artificial datasets instantly, enabling continuous model retraining, adaptive simulations, and rapid prototyping in dynamic environments like finance, retail, and logistics.
- Autonomous synthetic data pipelines: Future platforms will automatically detect data drift or gaps and generate updated datasets, ensuring that AI systems stay accurate and responsive to evolving trends.
- Tighter integration with AI development workflows: As synthetic data becomes a core component of AI pipelines, it will be more tightly integrated into MLOps processes, testing environments, and cloud infrastructures, ensuring seamless model experimentation, QA, and tuning.
How N-iX supports enterprise synthetic data initiatives
At N-iX, we help enterprises design and implement practical synthetic data solutions tailored to real-world use cases.
Whether you're constrained by data access limitations, privacy requirements, or insufficient training data, our teams build and integrate synthetic datasets that are statistically reliable, compliant with regulations, and ready for AI development, testing, and scale.
Backed by more than 200 data experts within a global team of 2,400 specialists, N-iX partners with enterprises to align synthetic data strategies with business goals and deliver AI solutions that create measurable, long-term value.
Strategy and architecture
We help define your synthetic data roadmap, aligning generation methods with compliance needs, data governance policies, and business goals. This ensures your synthetic data delivers both value and peace of mind.
Model development and validation
Our teams use advanced generative techniques to create datasets that retain critical relationships from the source data. We validate synthetic datasets to ensure statistical accuracy and realism, reducing the gap between development and deployment.
Seamless integration
N-iX integrates synthetic data workflows into your machine learning pipelines, CI/CD processes, and cloud environments. This allows your teams to train, test, and deploy AI models faster, with fewer data bottlenecks.
Continuous optimization
We monitor model performance, retrain generators, and evolve synthetic datasets to match shifting real-world conditions. This ensures your models stay current and effective in production environments.
Synthetic data won't replace real data, but it will redefine how enterprises innovate. With the right expertise and validation practices, it becomes a powerful enabler of faster R&D, safer data sharing, and more privacy-aware AI systems.
Have a question?
Speak to an expert