The telecommunications industry generates enormous volumes of operational, network, and customer data. Yet, turning this information into timely, reliable decisions is often challenging. Fragmented systems, slow reporting, and limited visibility across departments prevent operators from quickly addressing network issues, changes in customer behavior, and potential revenue risks.
This is where business intelligence in the telecom industry makes a difference. Instead of relying on static reports, BI creates a shared, real-time view of what is happening across customers, networks, and financial performance. Executives gain visibility they can act on, not days later, but while outcomes can still be influenced.
In business intelligence , success goes beyond dashboards. BI must be built on scalable architectures that integrate with complex OSS/BSS systems and adapt as telecom networks evolve. Done right, BI in the telecom industry becomes a strategic decision layer that strengthens efficiency, resilience, and long-term competitiveness.
This article explores how business intelligence in the telecom industry drives measurable business value, highlights the core capabilities most important to executives, and illustrates real-world impact through a case study of N-iX’s partnership with a European telecom operator.
Understanding business intelligence in telecom
Telecom networks produce high-volume, high-velocity data from billing systems, customer interactions, service usage, and network performance. Managing this data manually or through fragmented systems is impractical.
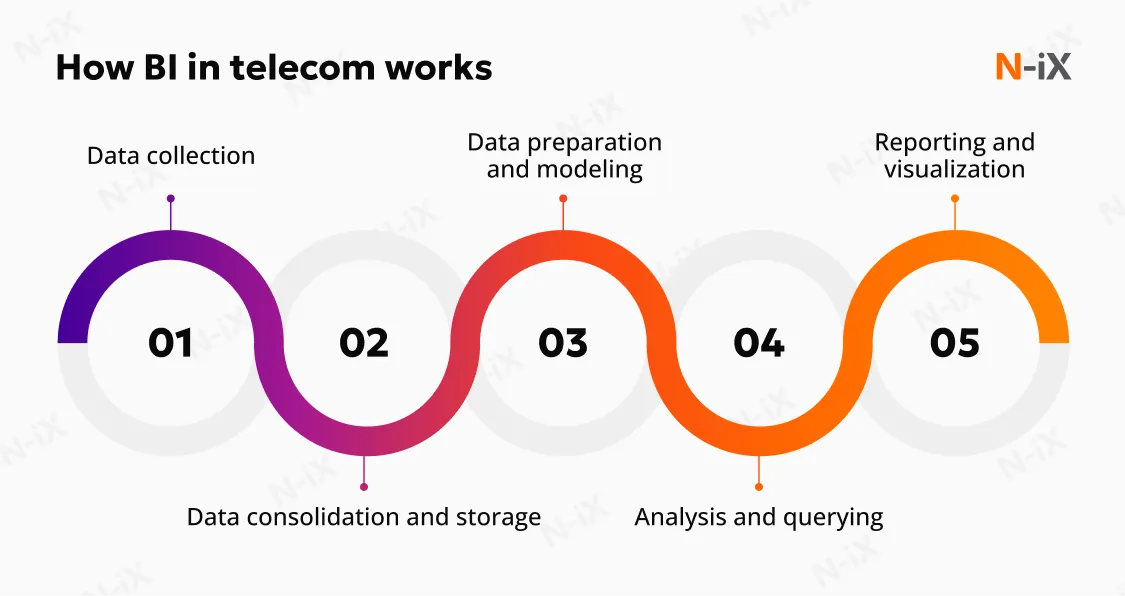
Business intelligence in telecom industry centralizes these streams, creating a unified view that allows companies to respond quickly to market shifts, service issues, and customer needs. Key processes include:
- Data collection: Aggregating information from network operations, CRM, billing, and support systems. External data adds business context.
- Data consolidation and storage: Centralized repositories act as a single source of truth, supporting large-scale querying and historical analysis.
- Data preparation and modeling: Structuring data into telecom-specific models: customers, plans, usage, and network performance ensures consistent analytics.
- Analysis and querying: Teams explore patterns in service, usage, operations, and revenue.
- Reporting and visualization: Dashboards display KPIs, trends, and exceptions in an accessible format, enabling faster, more confident decision-making.
Core capabilities of business intelligence in telecom
Data integration
Telecom environments are rarely simple. Network systems, billing platforms, CRM tools, and customer support software often operate independently. Business intelligence in telecom integrates these data sources into a unified analytical layer, enabling cross-functional insights without manual reconciliation.
Analysis, reporting, and visualization
Raw data alone doesn’t help decision-makers. Telecom analytics tools turn complex datasets into dashboards that highlight trends, exceptions, and risks. Stakeholders can quickly understand what’s changing and where attention is needed, without digging into technical reports.
Business performance management
BI plays a critical role in linking strategy to execution. Performance metrics tied to revenue, customer experience, and network reliability help leadership teams track progress and adjust priorities before issues escalate.
Self-service BI
Self-service capabilities enable employees to explore data independently, accelerating decision-making and reducing dependence on technical teams, which is critical in fast-moving telecom environments.
Network optimization
BI supports network planning and optimization by analyzing traffic volumes, congestion points, and service quality metrics, helping operators maintain reliability and control costs.
Customer segmentation and personalization
By analyzing usage and behavioral data, business intelligence for telecommunications enables precise customer segmentation, targeted offerings, and more relevant customer interactions.
Predictive maintenance and fault detection
Historical and real-time performance data help identify early signs of equipment degradation or service anomalies, reducing downtime and improving service continuity.
Read also about the use cases of agentic AI in telecom
Key applications of business intelligence in telecom operations
Business intelligence in the telecom industry delivers the most value when it is applied to tangible operational and commercial challenges. Below are the core telecom use cases where BI consistently supports measurable business outcomes.
BI-powered churn prevention
Customer churn threatens recurring revenue and increases acquisition costs. BI identifies at-risk subscribers early and enables targeted retention strategies.
How BI enables this: In practice, business intelligence for telecommunications brings all customer, billing, and service data together in one place. This unified view helps operators spot early warning signs of churn, such as changes in usage patterns or repeated service issues.
Business value: With early visibility into churn risk, telecom managers can prioritize retention where financial exposure is highest, deploy targeted offers instead of blanket discounts, and resolve service issues before dissatisfaction escalates. Even marginal reductions in churn translate into substantial revenue preservation at telecom scale, making churn analytics one of the highest-impact BI use cases.
Network optimization and performance management
BI in telecom industry supports monitoring of latency, throughput, packet loss, and SLA metrics. Real-time dashboards enable faster decision-making in 5G and advanced network environments.
How BI enables this: Business intelligence platforms continuously analyze network data to detect bottlenecks, anticipate failures, and optimize resource allocation. BI analytics for telecom support: monitoring key performance indicators such as latency, throughput, packet loss, bandwidth utilization, and quality-of-service metrics linked to SLAs.
Business value: By centralizing network performance insights into real-time dashboards, BI provides operations and leadership teams with a shared view of network health. This is especially critical in 5G environments, where network slicing, traffic prioritization, and service differentiation demand tighter operational control and faster decision-making.
Fraud detection and revenue assurance
Telecom fraud and revenue leakage represent material financial risk as traffic volumes and service complexity grow. BI-powered fraud detection and revenue assurance help operators protect margins, reduce losses, and maintain financial control across complex billing and partner ecosystems.
How BI enables this: Business intelligence for telecommunications identifies abnormal patterns in call activity, routing behavior, geographic usage, and billing data. Instead of relying solely on static rules, BI-driven analytics surface anomalies and trends that signal fraud or revenue leakage before they escalate into significant losses.
Business value: Beyond fraud prevention, BI supports revenue assurance by monitoring billing accuracy, validating invoices, and ensuring compliance with contracts and partner agreements. This consolidated view of revenue flows enables earlier intervention, tighter governance, and more predictable financial outcomes.
Customer segmentation and personalization
Generic offers limit revenue potential and increase churn risk. BI-driven customer segmentation enables telecom operators to improve relevance, increase ARPU, and strengthen customer loyalty through data-informed personalization.
How BI enables this: By analyzing demographic, behavioral, geographic, and usage data, telecom business intelligence platforms group customers based on shared characteristics and needs. Advanced BI environments support dynamic segmentation, allowing customer profiles to evolve based on real-time usage and interaction data.
Business value: Effective segmentation enables more precise pricing, tailored service bundles, and lifecycle-based engagement strategies. Instead of one-size-fits-all offers, telecom providers align services with actual customer behavior and demand patterns, supporting sustainable revenue growth and competitive differentiation.
BI tools and platforms used in telecom
The following overview highlights key categories of telecom analytics tools that support enterprise-scale BI, real-time customer insights, and cloud-based analytics.
|
Category |
BI platform |
Value for telecom |
Use cases |
|
Enterprise BI for large operators |
Qualtrics XM |
Enterprise-scale analytics with centralized governance and regional flexibility |
Predictive churn analysis, CRM-integrated insights, multilingual sentiment analysis |
|
Real-time customer experience analytics |
SurveySensum |
Immediate visibility into customer sentiment |
NPS tracking, closed-loop feedback management, churn prevention |
|
Cloud-based BI platforms |
Power BI, Tableau, Looker, Domo |
Faster time-to-value and scalable analytics |
Network performance dashboards, revenue monitoring, executive reporting, predictive insights |
Learn more about the key differences between business intelligence vs data analytics
Challenges of implementing BI in the telecom
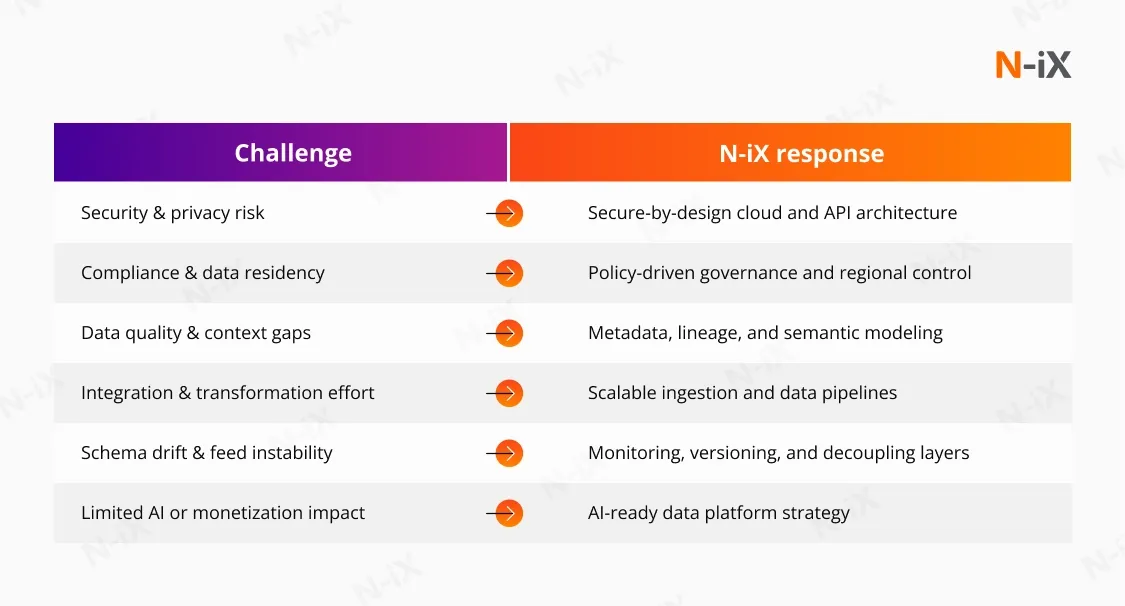
Business intelligence is no longer optional for telecom operators. It underpins network reliability, customer experience, revenue assurance, and operational efficiency. However, implementing BI at telecom scale presents distinct challenges driven by data volume, system complexity, and organizational constraints. Below are the most common BI challenges telecom companies face, along with practical approaches to address them.
Fragmented data sources and inconsistent data structures
Telecom operators work with data from network systems, billing platforms, CRM solutions, customer support tools, and external sources. These systems often use different formats, schemas, and update cycles, making unified analysis difficult. Without consolidation, analytics remain siloed and unreliable.
How N-iX helps: We design centralized BI architectures that integrate heterogeneous telecom data into a single analytical environment. This includes:
- Implementing scalable data lakes to ingest raw data in native formats
- Establishing standardized data models for analytics and reporting
- Introducing Master Data Management (MDM) to create a consistent “golden record” across systems
This approach enables cross-functional analytics while remaining flexible enough to scale with growing data volumes.
Poor data quality undermining BI outcomes
Duplicate customer records, incomplete call detail records, and billing inconsistencies directly impact reporting accuracy and decision-making. In telecom, even small data-quality issues can lead to significant revenue leakage or inaccurate performance assessments.
How N-iX helps: Our team addresses data quality at the system level rather than through manual fixes:
- Automated data cleansing and validation pipelines
- MDM-based synchronization of critical customer and contract data
- Continuous data quality monitoring to detect anomalies early
Slow data processing and limited timeliness of analytics
Telecom operations depend on timely insights. When data ingestion and processing take hours or even days, analytics become operationally irrelevant. This affects network monitoring, fraud detection, and service performance analysis.
How N-iX helps: We evaluate BI platforms and data architectures against actual telecom workloads. Where legacy systems become bottlenecks, the team:
- Redesigns data pipelines for parallel and distributed processing
- Replaces monolithic data warehouses with scalable analytical databases
- Optimizes ingestion and transformation workflows for near real-time analytics
Maintaining analytical models and business logic over time
Telecom analytics continues to advance as customer behavior, service usage, and pricing models evolve. Without proper monitoring, analytical models and business rules become outdated, leading to misleading insights and poor strategic decisions.
How N-iX helps: Rather than focusing on individual models, N-iX builds governance frameworks around analytics, including:
- Performance monitoring of analytical outputs
- Versioning and documentation of business logic
- Regular validation of assumptions against real operational data
This ensures analytics remain aligned with real-world telecom conditions, such as seasonal usage patterns or changes in tariff structures.
Limited adoption of self-service BI across the organization
While self-service BI promises faster decision-making, telecom companies often see adoption limited to a small group of analysts. Other teams remain dependent on manual reports, slowing operations and reducing BI value.
How N-iX helps: We focus on usability and adoption, not just tool deployment. This includes:
- Selecting BI platforms aligned with business-user capabilities
- Designing role-based dashboards for different teams
- Supporting rollout with documentation, training, and post-launch support
The goal is to make BI a shared operational asset rather than a centralized reporting function.
Organizational and regulatory considerations
Beyond technical challenges, telecom BI initiatives must account for:
- Regulatory requirements related to data privacy and security
- Scalability constraints driven by rapid data growth
- Cultural resistance to data-driven decision-making
N-iX addresses these factors through strong data governance design, scalable architectures, and close collaboration with business and compliance teams to ensure BI solutions are both usable and compliant.
Discover top 10 telecom industry trends to watch in 2026
Why N-iX
Business intelligence in telecommunications is no longer just a reporting tool added at the end of projects. It’s a core capability that must work across networks, customers, operations, and finance without slowing the business.
Delivering this at enterprise scale requires more than dashboards; it demands deep domain expertise and seamless transformation without disrupting critical systems. N-iX works with telecom organizations that need business intelligence for telecommunications at scale, not isolated analytics initiatives. With 200 data and AI engineers and over 60 delivered data initiatives, our teams focus on production-ready BI environments that integrate with OSS/BSS systems, meet regulatory requirements, and remain flexible as networks modernize.
By leveraging BI across customer operations, network performance, revenue assurance, and strategic planning, operators gain:
- Faster response to operational risks
- More effective customer retention
- Tighter financial control
- Scalable analytics that support long-term transformation
To illustrate how N-iX turns BI expertise into measurable business outcomes, here’s an example from our work with a European telecom operator.
Faster time-to-market through full-scale digital transformation
Challenge: As Lebara expanded across multiple European markets, fragmented systems, delayed BI reporting, and on-premises infrastructure slowed decision-making and limited scalability.
N-iX approach: We partnered with Lebara to modernize its commerce platforms, migrate core systems to a multi-cloud architecture, and rebuild BI and data pipelines to deliver near-real-time insights.
Value delivered:
- Accelerated time-to-market for new digital services
- Improved operational visibility across multiple countries
- Reduced infrastructure and support costs
- Optimized BI report generation and removed delays with data lake development
- Established a scalable foundation for omnichannel customer experiences, advanced analytics, and continuous product innovation
Final thoughts
Business intelligence in telecom is a strategic enabler that drives growth, operational resilience, and exceptional customer experiences. N-iX helps telecom operators transform fragmented data into a single, actionable decision layer that scales across networks, customers, and operations.
If you’re looking to unify data, improve decision speed, and scale analytics across networks and markets, N-iX can help design and deliver a BI foundation that grows with your business.
FAQ
What is business intelligence in the telecom industry?
Business intelligence in the telecom industry becomes relevant when fragmented data and slow reporting begin to limit decision speed and operational control. It connects network, customer, billing, and financial data into a unified decision layer, allowing telecom leaders to act on issues and opportunities while outcomes are still within their control.
How is business intelligence in telecom different from traditional reporting?
Traditional reporting looks backward and explains what already happened. Business intelligence in telecom supports ongoing decision-making by integrating OSS/BSS data, enabling near real-time analytics, and embedding insights into operational and strategic workflows rather than static dashboards.
When does telecom business intelligence deliver the most value?
Telecom business intelligence delivers the highest value when applied to recurring, high-impact decisions such as churn prevention, network performance management, revenue assurance, and customer segmentation. These areas combine high data volume with direct financial or operational risk, making timely insights critical.
Have a question?
Speak to an expert