Healthcare stands at a promising turning point: Routine tasks and administrative work still consume specialists' time, yet modern technology can streamline much of it instantly. With rising demand, the sector is ready for solutions that enhance efficiency and the quality of care.
This is where the shift from AI assistants to AI agents becomes pivotal. Assistants wait for instructions; agents run entire workflows. And in healthcare, those workflows (scheduling, lab coordination, patient communication) are exactly what bog down staff the most. Today's clinically reliable agents simplify operations and reduce bottlenecks, delivering faster care and better outcomes.
For enterprises ready to adopt agentic AI in healthcare, AI agent development services help determine which processes to automate, where agents add the most value, and how to integrate them safely and effectively.
Let's dive into what AI agents are, how they function, and where they deliver the biggest impact.
AI agents in healthcare explained
AI healthcare agents are action-enabled digital assistants that support clinicians by handling defined tasks within administrative and clinical settings. They interpret requests, gather information from multiple systems, and complete multi-step actions while keeping healthcare professionals in control.
Powered by large language models (LLMs) and trained on clinical datasets, agents operate through conversational interfaces (chat, voice, or text). They understand medical context, summarize interactions, and flag critical issues for human review. When integrated into real operations, they automate time-consuming tasks like patient intake, form completion, documentation, and appointment preparation.
Advanced agents also detect anomalies in lab results or identify high-risk patients by analyzing both historical and real-time data. Cloud infrastructure is vital for enabling these capabilities, providing scalability, processing power, and access to distributed health data.
Adoption is still early due to interoperability and regulatory complexity. Nonetheless, the healthcare AI market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 38.6% and reach $110.61B by 2030 compared to $21.66B in 2025. What started as pilots is now progressing into operational infrastructure across clinics, labs, and support centers.
The technology behind medical AI agents
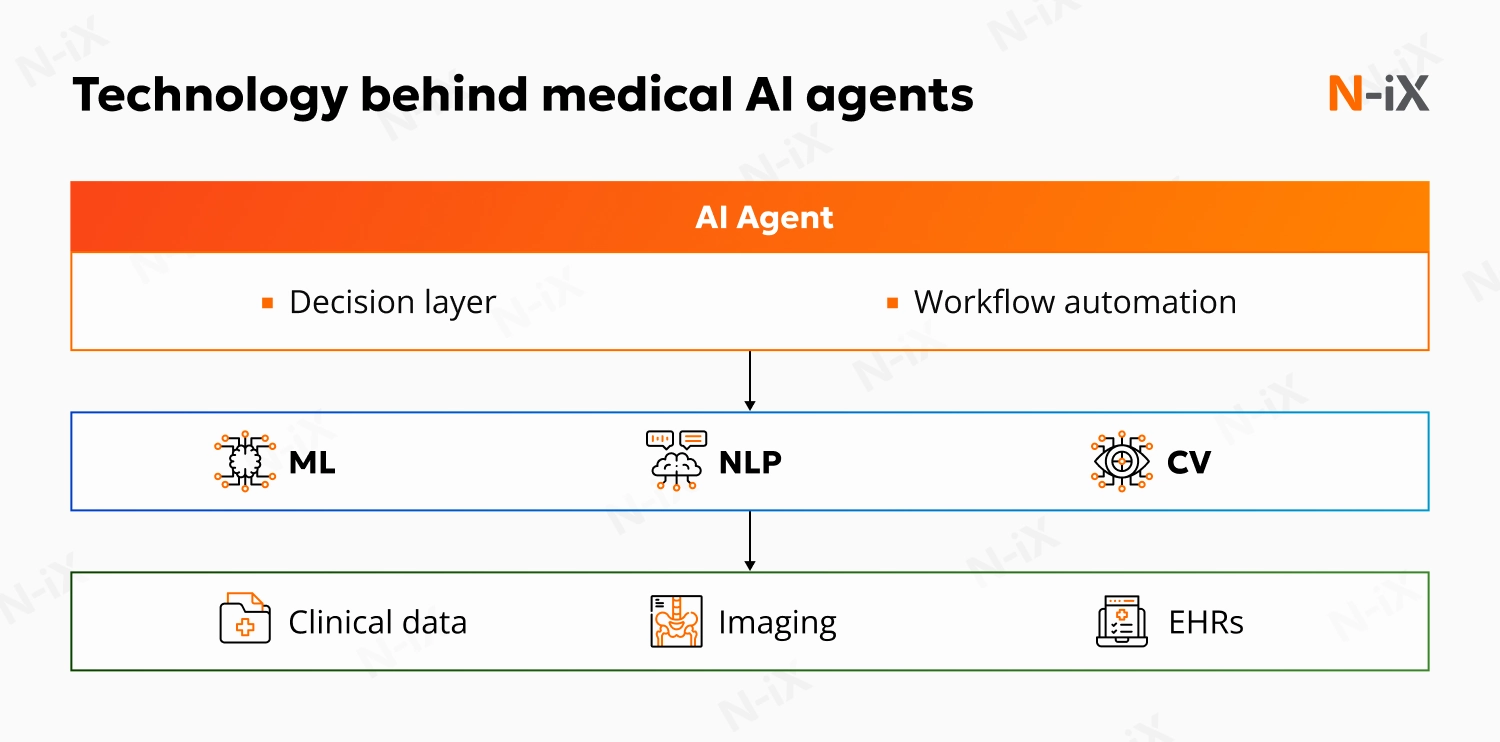
Healthcare AI agents rely on three core technologies:
- Machine Learning (ML): Learns from structured and unstructured healthcare data to identify patterns, assist in diagnostics, and make care recommendations. Continuously improves with more input.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Understands and interprets clinical language to generate structured summaries, populate EHRs, and communicate with users in natural language.
- Computer Vision: Reads and interprets medical imagery (X-rays, MRIs, pathology scans), flagging potential issues and acting as a diagnostic aid.
Together, these technologies enable AI agents in healthcare to fit seamlessly into clinical environments without disrupting core systems.
Discover where generative AI delivers the most value in healthcare—get the guide!


Success!

Types of AI agents healthcare
- Conversational agents that manage scheduling, answer patient inquiries, and support engagement via chat, text, or voice.
- Document and data processing agents extract and validate data from EHRs, clinical notes, labs, and insurance forms.
- Predictive & risk-scoring agents analyze historical and real-time data to flag patient risks and detect emerging patterns.
- Compliance and monitoring agents automate data audits, permissions checks, and alignment with regulatory/payer requirements.
Learn more: Computer vision in healthcare: trends, use cases, and reasons to adopt
How AI agents drive value in healthcare
|
Focus |
Problem |
AI agent solution |
Value |
|
Clinician support |
Staff is overwhelmed by the administrative workload |
Summarizes patient history, surfaces insights from specialized datasets, and assists in predictive modeling |
Reduces burnout and boosts efficiency |
|
Diagnostics |
Delayed/missed diagnoses |
Analyzes EHRs, labs, and imaging |
Faster, more accurate diagnoses |
|
Personalized treatment |
Generic treatments |
Builds patient-specific care plans |
Delivers more effective, tailored therapies |
|
Operational efficiency |
Time lost on manual updates |
Automates documentation and data entry |
Reduces 36% of clinicians' clerical tasks, freeing time for patient care and coordination |
|
Cost control |
High overhead costs |
Streamlines billing and reimbursement |
Reduces expenses without harming care |
|
Patient monitoring |
Limited oversight post-visit |
Tracks vitals and flags risks |
Improves safety with proactive care |
|
Research acceleration |
Slow drug development |
Automates eligibility and trial analytics |
Speeds discovery and clinical validation |
|
Accessibility |
Barriers to patient engagement |
Supports communication, reminders, and scheduling |
Enhances care access and responsiveness |
Agentic AI use cases in healthcare
When most people hear "AI agent," they usually imagine a chatbot that answers questions or books an appointment. But modern agentic AI in healthcare goes far beyond that: it supports, or even completely takes over, entire workflows that used to drain hours from clinical and admin teams.
Taking over clinical and administrative tasks
AI agents for healthcare work almost like additional staff: reading insurance cards, checking eligibility, filling out lab forms, sending results, generating bills, completing documentation, and doing it all without slowing down.
Medical organizations already using AI agents report that intake and documentation time has dropped, while manual report generation has become almost nonexistent. Agents can even forecast patient volume and acuity, enabling managers to plan staffing more effectively.
Orchestrating data and workflow routing
Agents operate silently behind the scenes to manage complex workflows. For instance, when a patient submits a form with an urgent concern, the AI can flag the issue, create a triage task, notify the right clinician, and even rearrange the day's schedule. These behind-the-scenes actions reduce mental fatigue and improve operational responsiveness.
Clinical decision support
AI agents can analyze records, imaging data, and patient histories to support earlier diagnosis, preventive treatment, and second opinions. AI continuously learns from new outcomes and medical research, refining recommendations over time. A standout example is Prenosis, the first AI-powered device for diagnosing sepsis. It analyzes a dataset of 100,000+ blood samples from 25,000 patients and uses 22 clinical indicators to alert clinicians when a patient is at risk.
Continuous monitoring and patient engagement
Humans can't monitor patients 24/7, but AI can. Personal health agents track symptoms, send medication reminders, follow up after discharge, and escalate when something looks wrong. In emergencies, they can even trigger an ambulance dispatch. AI diagnostics are also advancing fast. Some systems now detect tuberculosis on chest X-rays with 98% accuracy, outperforming radiologists in 96% of test cases and doing it in seconds.
Radiology and image automation
AI agents analyze imaging studies such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, identifying subtle anomalies and prioritizing urgent cases for review. Platforms like Aidoc autonomously flag critical conditions, improving turnaround times and diagnostic consistency while enabling radiologists to focus on complex cases.
Drug discovery and development
Drug development, traditionally slow and costly, is accelerated through agentic AI. These systems autonomously explore chemical and biological datasets, design candidate compounds, and run virtual experiments, dramatically compressing timelines. Companies like Exscientia have leveraged this approach to develop drug candidates in months rather than years, demonstrating the potential to transform pharmaceutical research.
AI-powered robotic surgery assistants
Robotic assistants progressed from human-guided tools into semi-autonomous agents. They combine advanced robotics, computer vision, and ML to help surgeons with specific medical tasks. Beyond guidance, they can autonomously adjust movements during procedures based on patient-specific anatomy. Systems like Mazor X and the da Vinci Surgical System combine robotics, computer vision, and agentic AI to standardize surgical outcomes while reducing risk.
Discover more about AI agent use cases
Common pitfalls when implementing agentic AI in healthcare
AI-powered healthcare agents have tremendous potential, but many initiatives stall before they ever reach production. Not because the technology is inefficient, but because the surrounding systems, processes, and constraints aren't ready. Here are the common pitfalls, along with the ways N-iX supports organizations in addressing them.
Starting with a chatbot UI instead of workflow integrations
Chatbots are easy to demo, which is why many projects start there. But without proper integration into EHRs, lab systems, scheduling, billing, and payer platforms, a chatbot can only talk, not act. A UI without backend connections just adds another layer rather than reducing work.
How N-iX helps: We help connect the agent to the systems it needs to operate securely and with minimal disruption. The goal isn't to amaze users with a chatbot, but to ensure the agent can perform actual tasks in the background.
Overlooking security and compliance
Many off-the-shelf AI tools weren't designed for PHI (Protected Health Information), and issues usually surface late during legal review or security audits. Missing controls such as encryption, access restrictions, or audit logs are a common challenge when implementing agentic AI in healthcare.
How N-iX helps: We design and implement AI systems with HIPAA, GDPR, and local data-protection frameworks. That includes secure data flows, access control, auditability, and privacy safeguards.
AI that fails in real conditions
Many early pilots run smoothly in clean test scenarios. Then they run into real cases:
- incomplete patient data
- missing insurance details
- schedule conflicts
- exceptions to exceptions
If the agent wasn't designed to handle ambiguity or to escalate appropriately, staff end up doing extra work to fix the agent's mistakes.
How N-iX helps: We don't aim to create agents that "handle everything." Instead, we design them to handle clear, repetitive tasks and hand off the rest to humans without disruption. The focus is on reliability, not perfection, agents that help, not agents that get in the way.
Partnering with N-iX to build reliable AI agents
At N-iX, we help enterprises move from concept to value through agentic AI. With a team of 200 data experts, we design AI agents that not only sound impressive but also perform reliably, safely, and at scale.
Whether you're improving diagnostics, reducing operational costs, or accelerating research, we guide you in choosing the proper use cases, ensuring secure integrations, and building systems that align with your business goals and compliance requirements.
Have a question?
Speak to an expert




