With ecommerce becoming the primary channel for digital retail, it’s getting more and more challenging for merchants to tackle privacy and security issues. High volumes of credit card and bank account data, as well as large stores of personally identifiable information, make ecommerce platforms a lucrative target. It’s no surprise that 98% of online merchants reported experiencing at least one form of cyber attack in 2025. [1] In this environment, proactively addressing security issues in ecommerce is critical to protecting revenue, reputation, and customer trust.
So, what are the most common types of security vulnerabilities in ecommerce that retailers should watch out for? And how can you protect yourself and your customers from these threats? Find the answers in our expert guide.
Key security issues in ecommerce and how to fix them
#1 Online payment fraud
The shift to online and card-not-present (CNP) transactions has contributed to numerous security vulnerabilities in ecommerce. While physical card theft has declined, fraud has moved into digital channels, where attackers exploit stolen credentials, compromised identities, and frictionless checkout flows.
Common types of online payment fraud include:
- Identity theft: Fraudsters obtain personal and login data through phishing, social engineering, or data breaches, then impersonate legitimate customers to place unauthorized orders.
- Friendly fraud: A legitimate cardholder disputes a transaction after receiving the goods, either intentionally or accidentally, making it difficult for retailers to distinguish between genuine chargebacks and refund abuse.
- Clean fraud: Transactions appear legitimate because attackers use complete, accurate customer data, allowing them to bypass basic verification checks.
- Card testing: Attackers use automated tools to run small authorization attempts in order to verify stolen card details before using them for larger fraudulent purchases.
Together, these types of security vulnerabilities in ecommerce make up the dominant share of all incidents. Most retail organizations encounter at least one of them in a typical year, which is why they consistently appear at the top of incident reports. The chart below shows how frequently each vulnerability occurs.

So, what can you do to combat payment fraud? Our ecommerce experts share several effective security measures.
How to prevent it:
- Use AI-driven fraud detection early in the process: AI-based systems can analyze transaction patterns, user behavior, and contextual signals in real time to flag anomalies before payments are completed. It’s important to ensure transparency and explainability in these decisions, especially for customer-facing actions.
- Maintain PCI compliance or rely on compliant payment providers: Ensuring that card data is transmitted and stored securely is a baseline requirement, whether handled internally or delegated to a trusted PCI-compliant payment service provider.
- Apply risk-based authentication and verification controls: Multi-factor authentication, step-up verification for high-risk transactions, and selective use of AVS and CVV checks help balance fraud prevention with a smooth user experience.
- Secure data in transit and at rest by default: All payment-related communications should use modern encryption standards and HTTPS to prevent interception and tampering with sensitive customer information.
- Reduce chargeback exposure through monitoring and review: Regular analysis of dispute patterns and transaction outcomes helps identify emerging fraud tactics and refine prevention rules.
#2 Misconfigurations of web applications
Modern ecommerce environments rely on multiple interconnected web applications, APIs, and third-party services. Together, they power product catalogs, customer accounts, shopping carts, and checkout flows. When these components are misconfigured or deployed with insecure defaults, they become a common source of security issues in ecommerce. In many cases, the problem is not immediately visible, but it leaves small gaps that attackers can later turn into a large compromise.
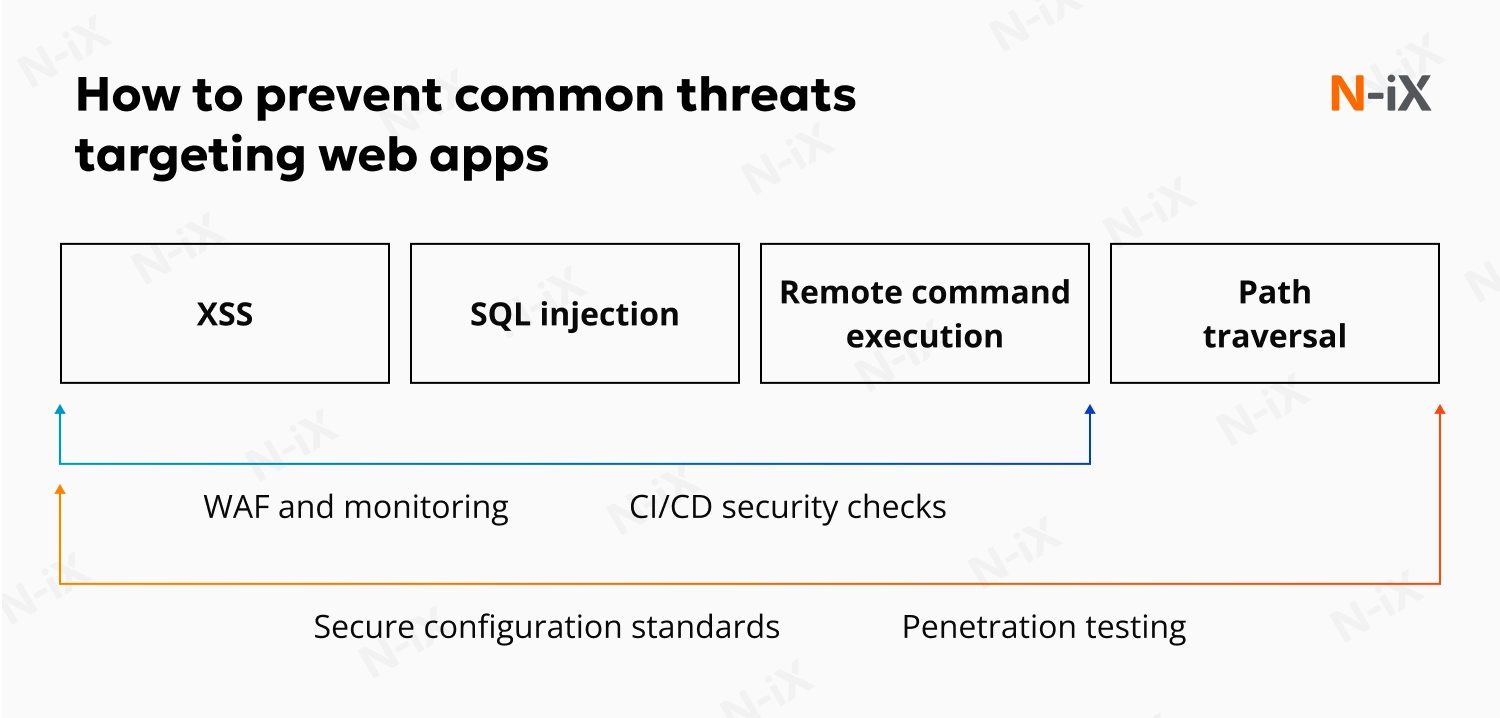
Common attacks targeting web applications include:
- Cross-site scripting (XSS): A client-side code injection attack that allows attackers to execute malicious scripts in a user’s browser and steal session data or manipulate user actions.
- SQL injection: The insertion of malicious SQL statements through unsanitized input fields, enabling attackers to read, modify, or delete data stored in backend databases.
- Insecure cookie handling: Improperly configured cookies can be modified or intercepted, allowing attackers to hijack user sessions or gain unauthorized access to accounts.
- Remote command execution: A vulnerability that allows attackers to run arbitrary commands on the operating system through a misconfigured or poorly secured application component.
- File-path traversal: A technique that exploits poor input validation to access files and directories outside the intended scope of the application.
These risks rarely stem from a single coding mistake. More often, they result from inconsistent security controls, overlooked configuration settings, or gaps in the development and deployment lifecycle. Over time, such weaknesses introduce different types of security vulnerabilities in ecommerce platforms, undermining customer trust, disrupting operations, and exposing sensitive data.
To ensure that web applications are secure against malicious threats, our experts recommend the following safeguards.
How to prevent it:
- Apply secure configuration standards across all environments: Ensure that applications, frameworks, and services are deployed with secure settings by default, and that all environments, from development to production, follow consistent security baselines.
- Use continuous monitoring and application-level protection: Web Application Firewalls (WAF) and runtime monitoring tools help detect and block malicious requests, misused endpoints, and abnormal application behavior.
- Test applications regularly with penetration testing and scanning: Controlled penetration testing helps identify exploitable misconfigurations and exposed endpoints that automated checks or code reviews might miss.
- Protect session data and client-side storage: Avoid storing sensitive or critical information in cookies, enforce secure and HTTP-only flags, and encrypt any client-side data that must be retained.
- Integrate security checks into the delivery pipeline: Automated configuration validation, dependency scanning, and policy enforcement within CI/CD pipelines reduce the risk of insecure changes reaching production.
#3 Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks
DDoS attacks disrupt the availability of an online system by overwhelming it with traffic generated from large numbers of compromised devices. For ecommerce businesses, the impact is rarely limited to a complete outage. DDoS attacks often degrade website performance, slow down checkout flows, or make critical services unavailable, directly affecting revenue and customer experience.
What makes DDoS particularly challenging is that malicious traffic can closely resemble legitimate user activity. During peak periods, such as sales campaigns or seasonal promotions, sudden spikes in traffic are expected. Distinguishing these from attack traffic requires careful analysis and dedicated tools, which is why DDoS remains one of the persistent security issues in ecommerce.
So, what are the steps you can take to prevent and mitigate DDoS attacks?
How to prevent it:
- Implement a DDoS mitigation solution: Purpose-built DDoS protection services analyze traffic patterns in real time and filter out malicious requests before they overwhelm applications or infrastructure.
- Use distributed, edge-based traffic protection: Content delivery networks and global points of presence help absorb large traffic volumes and reduce the impact of volumetric and application-layer attacks.
- Implement intelligent traffic filtering and rate limiting: Behavioral analysis and adaptive thresholds help identify abnormal request patterns without blocking legitimate users during high-traffic events.
- Deploy load balancing across applications and regions: Load balancers distribute incoming traffic across multiple instances or locations, improving resilience and maintaining availability even under attack conditions.
- Continuously monitor availability and performance metrics: Early detection of latency spikes, error rates, and service degradation enables faster response and limits business impact before customers are affected.
#4 Malicious bots and automated attacks
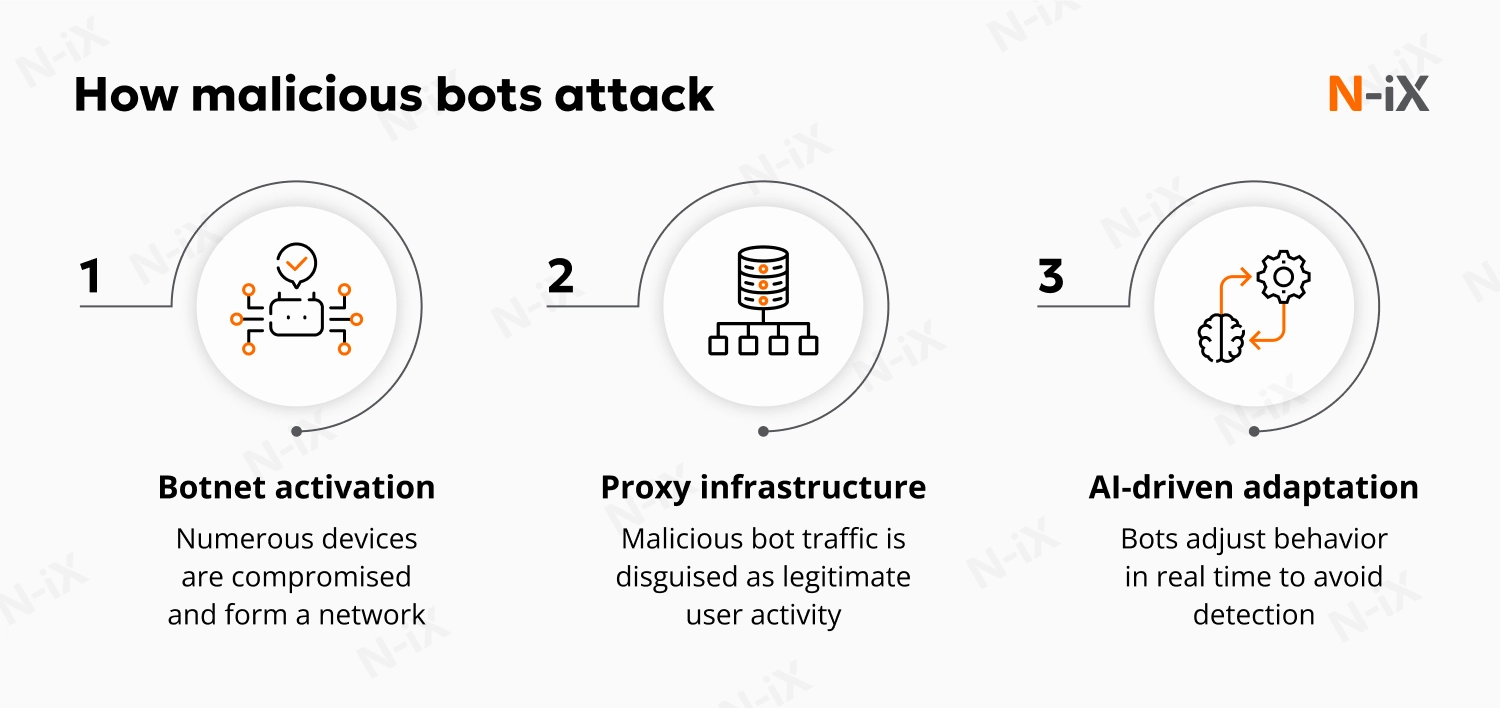
Automated traffic has become a permanent part of ecommerce operations, but not all of it is benign. Malicious bots increasingly mimic real users and operate at scale, enabling account abuse, inventory manipulation, price scraping, and checkout disruption. For retailers, this often translates into lost revenue and distorted analytics.
This threat is one of the most persistent information security issues in ecommerce because modern bots are no longer simple scripts. They rely on AI-driven automation to adapt their behavior in real time, rotate identities, and blend into normal traffic patterns. As automation grows more sophisticated, separating legitimate customers from malicious activity becomes harder, making bot-driven abuse one of the recurring security issues in ecommerce.
If you want to protect yourself against bot-driven attacks, our experts recommend several effective steps you can take to start addressing the issue.
How to prevent it:
- Continuously analyze traffic behavior: Monitoring how users interact with pages, APIs, and checkout flows helps identify patterns that deviate from normal customer behavior.
- Investigate unusual spikes and interaction anomalies: Sudden increases in traffic, repeated actions, or abnormal navigation paths often indicate automated activity rather than organic growth or campaign-driven demand.
- Monitor authentication and account activity closely: High volumes of failed logins, rapid account access attempts, or repeated credential checks are strong indicators of automated abuse.
- Protect APIs and mobile application backends: Bots frequently target exposed APIs and mobile endpoints, which often lack the same level of visibility and protection as web interfaces.
- Use AI-driven detection to identify intent: Machine Learning security tools analyze behavior patterns and interaction signals to distinguish humans from automation, adapting detection logic as attackers refine their techniques.
Discover more effective practices to overcome AI-driven security risks
#5 Account takeover (ATO)
Account takeover happens when attackers gain access to real customer accounts and use them as if they were legitimate users. Unlike payment fraud or DDoS attacks, this type of abuse is easy to miss at first. Logins succeed, actions look familiar, and the activity blends into everyday traffic. Over time, it leads to unauthorized purchases, drained loyalty balances, and frustrated customers, which is why account takeover remains one of the most common security vulnerabilities in ecommerce systems.
In practical terms, payment fraud targets individual transactions, while account takeover targets ongoing customer relationships, making early detection and response especially important.
How to prevent it:
- Watch for abnormal account behavior: Monitoring changes in login locations, devices, and session patterns helps identify compromised accounts even when credentials are technically correct. For example, a customer account logging in from a new country and immediately changing delivery details is a common warning sign.
- Strengthen authentication for high-risk actions: Requiring additional verification for password resets, checkout, or profile updates limits how much damage an attacker can do after gaining access to an account.
- Limit the impact of credential reuse: Controls like rate limiting, login attempt monitoring, anomaly detection, and basic password hygiene make it harder to abuse leaked credentials across multiple accounts.
- Respond to suspicious account activity quickly: Automated alerts, temporary account restrictions, and clear recovery workflows help stop misuse before customer trust is lost and support costs escalate.
#6 E-skimming
E-skimming is one of the most dangerous security issues in ecommerce. Attackers inject malicious JavaScript code into checkout or payment pages to capture card data as customers enter it. E-skimming commonly enters through compromised third-party scripts, misconfigured integrations, or vulnerable frontend components, making it a persistent class of cybersecurity threats in ecommerce.
N-iX experts note that preventing e-skimming attacks requires visibility and control over everything that executes in the customer’s browser, not just backend systems.
How to prevent it:
- Monitor client-side JavaScript: Regularly inspect first- and third-party scripts on checkout and payment pages to detect unauthorized changes or injected code early.
- Limit and govern third-party integrations: Reduce unnecessary scripts, review vendor security practices, and ensure external code is loaded only from trusted, verified sources.
- Apply strong access controls and MFA: Protect administrative accounts, deployment pipelines, and content management systems to prevent attackers from injecting malicious code through stolen credentials.
- Use script integrity and content security controls: Integrity checks and restrictive content policies help prevent tampered scripts from executing in users’ browsers.
- Monitor outbound connections and browser behavior: Watching for unexpected data transfers or calls to unknown domains can reveal active skimming attempts before large-scale data loss occurs.
How N-iX can help you prevent security issues in ecommerce
Modern ecommerce platforms are built for speed, scale, and convenience. That same combination also makes them a high-value target for attackers. With so many moving parts involved—continuous payment flows, customer accounts, and third-party integrations—risks can quickly add up.
Addressing security issues in ecommerce means looking beyond individual threats and understanding how weaknesses compound. To keep your systems resilient, security must be embedded across architecture, development, deployment, and day-to-day operations.
N-iX helps you strengthen ecommerce security by combining deep engineering expertise with extensive hands-on experience, having completed over 100 security projects for global technology leaders. Our teams conduct vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, application security reviews, and threat modeling to help you reduce breach risk, improve visibility into attack surfaces, and make informed security decisions. We can fully support you in building secure architectures, adopting DevSecOps practices, and maintaining compliance with industry and regulatory security standards.
References
1. 2025 Global eCommerce Payments & Fraud Report—Visa Acceptance Solutions