Large Language Models (LLMs) are becoming an important part of everyday business operations, but securing them is still a significant challenge. The latest LLM Security Report by Cobalt shows 32% of all vulnerabilities found in LLM pentests are high or critical—the top rate across all tested assets since 2022 [1]. Additionally, only 21% of critical issues are properly remediated, leaving 4 out of 5 vulnerabilities unfixed. This makes LLM applications one of the most challenging assets to secure, even for experienced teams.
What makes large language models so vulnerable? And how to detect and address LLM security risks? Our cybersecurity experts share the insights in this article.
Top 10 LLM security risks
Securing LLM systems begins with understanding which weaknesses attackers exploit most often. The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) shared a 2025 report on the most common LLM security vulnerabilities worldwide [2]. Here are the ten issues you should be aware of:

1. Prompt injection
This is one of the top LLM security risks businesses face. With carefully crafted instructions, an attacker can manipulate the model to ignore security rules, internal instructions, or system prompts. This can lead to policy circumvention, malicious instructions, or disclosure of prohibited information.
For example, an attacker can write a prompt that asks a model to disregard every rule it was given and display the admin password. If the system is not properly secured, it can reveal sensitive credentials.
2. Sensitive information disclosure
LLMs may unintentionally expose private or regulated data through direct output or indirect inference. Leakage can happen if training material includes real personal information or if conversation context is improperly retained.
3. Supply chain risks
AI systems depend on many external components, such as datasets, libraries, plugins, and pre-trained models. If any of these inputs are compromised, the entire application becomes vulnerable.
4. Data and model poisoning
Data poisoning represents one of the more advanced LLM security threats. Attackers modify training data or fine-tuning samples to influence model output. The model may learn harmful associations, embed backdoors, or reduce decision accuracy.
For instance, poisoning a dataset by inserting thousands of examples associating "approve" with fraudulent programs causes the model to approve risky or fraudulent transactions after deployment.
5. Improper output handling
Trusting LLM responses without validation can lead to harmful execution paths, wrong facts, and injection into downstream systems. Output must be moderated, sanitized, and checked before use.
6. Excessive agency
Granting too much system control to autonomous agents increases risk. Without oversight, an LLM might perform unintended actions such as sending messages, editing files, or executing workflows incorrectly.
7. System prompt leakage
System prompt leakage occurs when an attacker convinces an LLM to reveal its hidden instructions, policies, or internal behavior rules. With access to this information, the attacker understands how the system is controlled and can craft more effective jailbreak prompts to bypass restrictions. In practice, this makes safety filters easier to break and can lead to unauthorized access, data exposure, or harmful system behavior.
8. Vector and embedding weaknesses
LLMs interpret meaning through numbers, not words, so two different sentences can look very similar to the system even if they don't look alike to humans. Attackers can craft prompts or upload content that lands close to restricted information in this vector space, causing the model to retrieve or reveal things it should not. This means someone could access sensitive documents or bypass safety filters without ever using banned keywords directly.
9. Misinformation
Hallucinations and misinformation are among the leading LLM security risks today. Models may generate incorrect facts, fabricated references, biased claims, or persuasive but false explanations. Without verification, misinformation spreads quickly and may lead to harmful decisions.
10. Unbound consumption
Unbound consumption is a growing category of LLM security issues, particularly for production workloads. It arises when a model is pushed to use excessive computational resources, such as generating very long outputs or processing oversized inputs. An attacker can intentionally exploit this to overload the system, causing slowdowns or service outages.
In simple terms, it is like forcing the model to run endlessly until it crashes, and then using that to disrupt business operations, hide malicious activity, or damage reliability and stability.
Mitigate critical generative AI security risks—download the white paper!


Success!

Top 8 LLM security best practices
With a clear understanding of large language model security risks, you can prioritize actions to mitigate them. Here are the best practices N-iX security engineers recommend for protecting LLM applications:
Minimize and encrypt data
Try to minimize the data you send to the model. Reduce the amount of sensitive information you collect, store, or expose in prompts. Use practical techniques like masking, tokenization, pseudonymization, or differential privacy to filter out identifiers before they reach the LLM. This instantly lowers the impact of any potential breach or misconfiguration.
If minimization is not an option, ensure LLM data security with strong encryption. Manage encryption keys in dedicated systems such as cloud key management systems or hardware security modules. For high-risk workloads, our engineers recommend applying advanced options such as confidential computing. This method will enable keeping data encrypted while it is processed.
Enforce strong access controls
LLM systems should not be open to everyone in the company by default. Apply least-privilege principles so each person or service can access only the data, prompts, or models they need. Identity and access management methods, like role-based or attribute-based access control, work well here. Our security engineers also recommend integrating multi-factor authentication (MFA), strict identity validation, and zero-trust principles for every request.
Also, treat API keys and tokens like sensitive assets. Scope them tightly, rotate them often, and never share them across teams or environments. Add extra approval steps for administrative actions such as model deployments or safety-filter changes. These controls create a clear security boundary, making it easier to detect and stop unauthorized activity.
Moderate inputs and outputs
Most LLM-specific attacks start at the input layer. Prompt injection, prompt leaking, and jailbreaking occur when malicious text is directly passed to the model. Thus, it is crucial to validate and filter all inputs. Follow structured templates, limit free-form fields, and remove unwanted patterns before they affect system prompts or tools.
Outputs also require control. LLMs can unintentionally reveal sensitive data or generate harmful content if not monitored. Add safety filters and moderation tools that scan responses for personally identifiable information (PII), disallowed content, or policy violations. Apply post-processing to mask identifiers or force consistent formats, especially when outputs trigger automated actions. N-iX security experts also recommend conducting regular red-teaming to refine these guardrails and keep them effective.

Use privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs)
For workloads that handle highly regulated data, our security engineers recommend integrating privacy-enhancing technologies to provide additional protection. These relatively new methods can be very effective for addressing LLM security concerns and other AI-specific threats. One of the most common PETs is federated learning. It allows each environment to train the model locally on its own data. Instead of sharing raw records, systems send only summary updates back to a central coordinator. As sensitive information doesn't leave its original location, the risk of exposure is reduced.
More advanced PETs include homomorphic encryption and secure multi-party computation (SMPC). Homomorphic encryption allows certain operations on encrypted data without decrypting it first. SMPC lets multiple parties process shared information without exposing their individual datasets to one another. These methods are computationally heavy, so our engineers recommend applying them first to high-sensitivity use cases. When combined with standard controls, PETs help organizations meet stricter privacy regulations.
Build an LLM-specific incident response plan
Traditional incident response plans may not include cases with prompt injection, hijacking, or output misuse. Thus, you need playbooks that explicitly cover LLM-specific risks. Clearly define what counts as an incident, who is responsible for handling it, and how severity is determined.
During an actual event, teams should know exactly what to do: turn off affected keys, stop suspicious prompts, revoke compromised access, or roll back to a safe model version. Align your process with regulatory timelines such as GDPR's 72-hour reporting rule. Tabletop exercises using real LLM scenarios help identify gaps long before they cause downtime or data exposure.

Secure the SDLC and third-party ecosystem
To avoid most LLM security risks, embed protection into every stage of LLM development and deployment. Use application security testing and dependency scanning in CI/CD, and extend these checks to model registries, RAG connectors, and agent frameworks. N-iX security engineers advise listing all the third-party tools and monitoring them for vulnerabilities. To properly evaluate external vendors, check how they handle logging, training data, isolation, and incident reporting.
As LLM applications depend on many components, it is crucial to treat them like any other part of your software supply chain. Store them in registries, sign them, and track their origin. Add LLM-specific threat modeling early to understand where data enters, how it moves, and which parts of the system might be exploited.
Monitor and audit LLM activity
LLM security requires constant oversight. Set up continuous monitoring of prompts, outputs, and infrastructure to catch anomalies early. Centralize logs from model servers, APIs, vector databases, and safety filters in SIEM or XDR platforms. Define detection rules for activities such as unusual query spikes, repeated jailbreak attempts, or unexpected data access.
It is also important to complement monitoring with auditing. Review access permissions, test safety controls, and document how models evolve. Keep clear records of decisions, training datasets, and model updates. This transparency supports regulatory compliance and helps teams understand where risks grow and where additional guardrails may be needed.
Strengthen governance, compliance, and ethical oversight
Effective LLM programs run with transparent governance. Determine who makes decisions about risks, how new use cases get approved, and which standards every system must follow. Create an AI risk register that maps each project to its data sensitivity and regulatory impact. Use it to decide where stricter controls or human oversight are required.
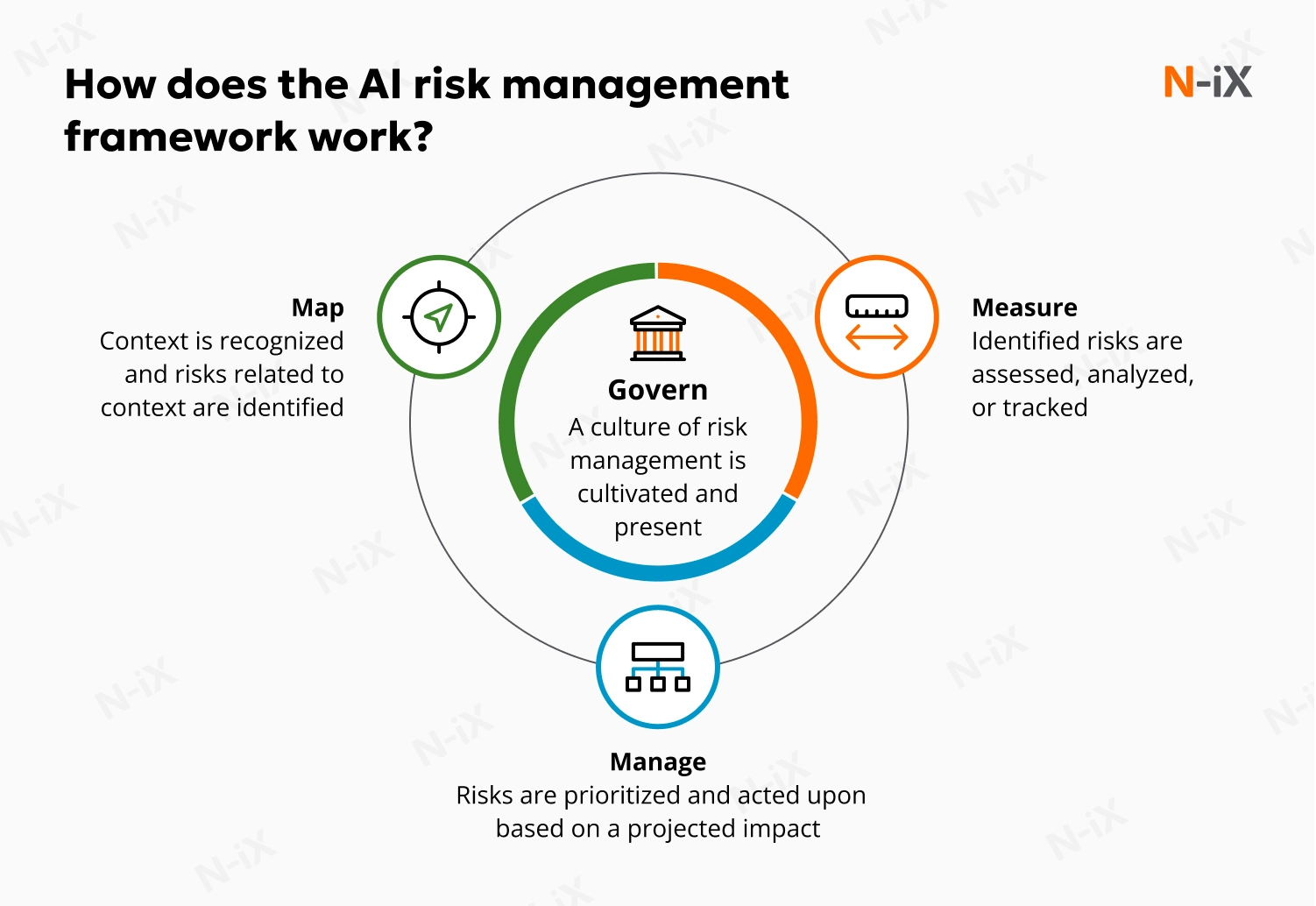
Ethical oversight is also necessary. Document rules for using AI responsibly, including transparency expectations, human-in-the-loop processes, and bias monitoring, and ensure teams follow them. Align these policies with AI risk management frameworks, such as NIST, or with industry guidance from OWASP. Involve security, data, legal, compliance, and product stakeholders in governance discussions. This keeps policies controlled, consistent, and aligned with organizational values.
How can N-iX help reduce LLM security threats?
Managing LLM security risks requires a deep understanding of LLM architectures, data flows, and emerging AI-specific threats. Partnering with a cybersecurity consultant can provide quicker access to specialized expertise and leverage it to address these vulnerabilities.
N-iX provides this support backed by 23 years of experience in software development and protection. We offer comprehensive security services for LLM initiatives, including secure architecture by design, data protection, model and prompt hardening, zero-trust access controls, AI-aware threat detection, and continuous monitoring. Every practice we implement is tailored to your infrastructure and workflows. With 100+ successful security projects and complete alignment with GDPR, CCPA, and SOC standards, N-iX helps you protect your LLM ecosystem without slowing innovation or operational efficiency.
Contact N-iX now and learn how we can help you reduce risks, meet compliance requirements, and build a safer foundation for your AI initiatives.
References
- State of LLM Security Report 2025 - Cobalt
- 2025 Top 10 Risk & Mitigations for LLMs and Gen AI Apps - OWASP
Have a question?
Speak to an expert





