Leveraging AI agents in cloud computing has become a game-changer for businesses seeking to automate operations, optimize resources, and drive innovation. According to a 2025 report from Cloudera, an impressive 96% of enterprises are expanding their use of AI agents, highlighting a significant shift toward intelligent, autonomous systems in everyday workflows.
But how can AI agents transform cloud services, and what challenges might organizations face? We will explore the primary use cases, AI agent platforms, and the main adoption challenges, providing actionable insights to help you leverage their full potential in the cloud.
Top 6 use cases of AI agents in cloud computing
Cloud platforms, with their on-demand scalability, advanced telemetry services, and programmable APIs, are an ideal foundation for AI agents. Here are six high-impact use cases illustrating how leveraging AI agents in cloud computing can transform business operations. We also supplemented them with N-iX expert guidance on customizing each approach to fit your environment.
1. Automated resource management and scaling
In cloud environments where compute instances and containers can scale rapidly, reactive AI agents can continuously analyze real-time metrics like CPU usage, memory, and network bandwidth directly from your cloud monitoring tools. By interacting directly with autoscaling APIs or serverless concurrency controls, intelligent agents adjust the size of clusters to accommodate fluctuations in demand. N-iX cloud experts advise starting agent implementation with a read-only "learning mode" in nonproduction accounts. Hence, the agent can observe typical usage curves before permitting it to enact scale-in and scale-out operations against your production autoscale groups or container orchestration clusters.
2. Intelligent monitoring and anomaly detection
Cloud providers centralize logs, traces, and performance counters in services like managed log analytics and distributed tracing platforms. By leveraging AI agents in cloud computing, teams can aggregate these data streams and detect correlations, such as a spike in query latency coupled with a slow-draining message queue. As part of a broader AIOps strategy, this approach enables continuous learning from operational data and proactive remediation of potential issues. N-iX recommends starting by routing anomalies flagged by an AI agent to an intermediate alerting system. Then, adjust the agent's sensitivity in low-risk environments before deploying it to monitor critical workloads.
3. Self-healing infrastructure and incident response
When virtual machines, container nodes, or serverless functions encounter issues, cloud APIs can interact with autonomous agents to take immediate action. Agents can promptly restart instances, recreate failed pods, or roll back to stable Infrastructure as Code (IaC) templates. To correctly implement agents into self-healing cloud infrastructure, N-iX experts recommend breaking down your existing remediation playbooks into small, safe steps. Then test these self-healing routines in isolated cloud environments, allowing agents to train and refine repair workflows without disrupting core services.
4. Cost optimization and workload scheduling
Cloud billing involves a complex combination of on-demand rates, reserved capacity, spot markets, and tiered storage charges. AI agents, familiar with these pricing models, can optimize costs by scheduling batch jobs during off-peak hours, utilizing low-cost spot instances, or identifying and flagging idle resources that don't align with active services. N-iX recommends setting monthly or quarterly cost-saving targets in your cloud governance plan. Then, integrate the agent's cost-saving recommendations into your central cloud management dashboard. This will enable finance and engineering teams to collaborate on balancing performance and cost trade-offs.
AWS, Azure, or GCP? Choose the best cloud for AI workloads!


Success!

5. Enhanced security and compliance management
Cloud security posture management relies on continuous auditing of IAM (identity and access management) policies, network security groups, and IaC pipelines. AI agents can detect configuration drift, such as open-by-default storage buckets or overly permissive roles, and then alert security teams or auto-remediate low-risk deviations. N-iX security consultants recommend codifying your strongest compliance controls as defenses in your cloud policy engine. Then, it is crucial to supplement them with AI agents to automatically enforce minor corrections while escalating high-impact issues to your incident management queue.
6. Intelligent migration
Migrating on-premises workloads to the cloud often faces delays at the discovery and sizing stages. AI agents accelerate this by analyzing server utilization, mapping network dependencies, and suggesting appropriately sized cloud instances or container configurations. N-iX experts recommend leveraging AI agents in cloud computing by following an iterative, pilot-first migration approach. Start by having the agent generate migration plans for a small application stack. Validate its resource estimates through a short test cutover, then use the feedback to fine-tune the agent's recommendations before proceeding with larger-scale migrations.
Read more: AI agent use cases: The missing piece in enterprise AI
Comparing key platforms for leveraging AI agents in cloud computing
Picking the right platform is crucial for deploying AI agents that smoothly integrate with your existing cloud architecture, scale on demand, and adapt to evolving workloads. Your choice should depend on factors like the desired level of integration, governance needs, and the trade-offs between ease of use and flexibility. Below is an overview of the most prominent offerings:
Amazon Web Services
AWS integrated agent features into SageMaker AI, Bedrock AgentCore, and its conversational AI portfolio. SageMaker Studio now enables end-to-end pipelines for tasks like data exploration, model training, and inference, functioning as autonomous agents behind the scenes. Bedrock provides one-click access to foundation models from Anthropic, Cohere, and Meta, streamlining the creation of proactive and collaborative agents without requiring infrastructure management. Additionally, Amazon Lex and the Amazon Q Developer simplify embedding interactive agents into platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or custom dashboards.
Choose Bedrock agents and SageMaker if you need:
- Highly customizable multi-step agent workflows with tight AWS integration;
- Complex multi-agent orchestration with memory and workflows;
- Integrated code execution in secure sandboxes;
- Strong enterprise-grade security and scalability through AWS infrastructure.
Microsoft Azure
Azure's ecosystem centers around a vision of agent orchestration through tools such as OpenAI Service, Cognitive Services for Language, and Bot Framework Composer. The OpenAI Service enables you to deploy conversational agents powered by GPT models, which can be enhanced with custom functions and integrated with your cloud data stores. Azure Logic Apps and Power Automate act as collaborative agents, automating multi-step business processes across SaaS and on-premises systems.
You can go with the Azure AI Foundry Agent Service if you want to leverage:
- Excellent compliance, security, and integration with Microsoft 365;
- Multi-agent workflows and code interpreter tools;
- Robust conversational agents;
- Easy GPT-based bot composers.
Learn more: Azure vs AWS AI: Evaluating cloud tools and services for your AI needs
Google Cloud Platform
Vertex AI is GCP's leading platform for building intelligent solutions, including AI agents. Vertex AI Agent Builder offers a platform for designing proactive "copilot" experiences using custom tools and open-source frameworks. With integrations like Cloud Functions, Workflows, and Pub/Sub event streams, you can quickly develop self-healing agents that address infrastructure alerts or data anomalies.
Opt for Vertex AI Agent Builder if you want to benefit from:
- No-code or low-code development for fast, enterprise-scale deployment;
- Built-in open-source frameworks like LangChain, LangGraph, or AG2 for multi-agent workflows;
- Deep integration with GCP tools (Cloud Functions, Pub/Sub, BigQuery);
- Open-ended generative AI developments.
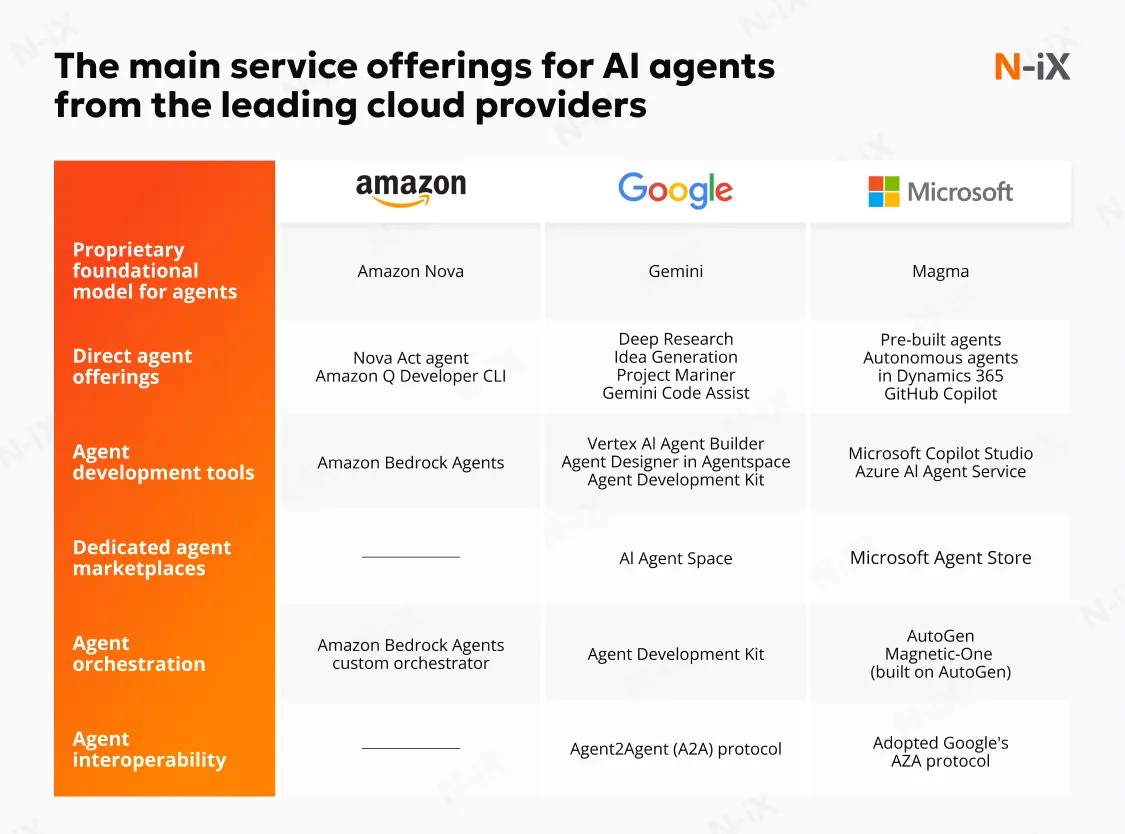
Specialist vendors and open-source frameworks
Beyond hyperscalers, platforms like OpenAI Function Calling, Anthropic Claude Instant, and Hugging Face Infinity provide lightweight agent runtimes deployable anywhere. IBM's Watson suite and Red Hat OpenShift deliver enterprise-grade, hybrid-cloud agent frameworks with built-in compliance and governance controls. Open-source toolkits like LangChain, Rasa, and AutoGPT empower cloud engineers to design custom workflows, coordinate tool interactions, and manage multi-agent dialogues without vendor lock-in.
Read also: How to build multi-agent AI system
Challenges to consider when adopting AI agents in the cloud
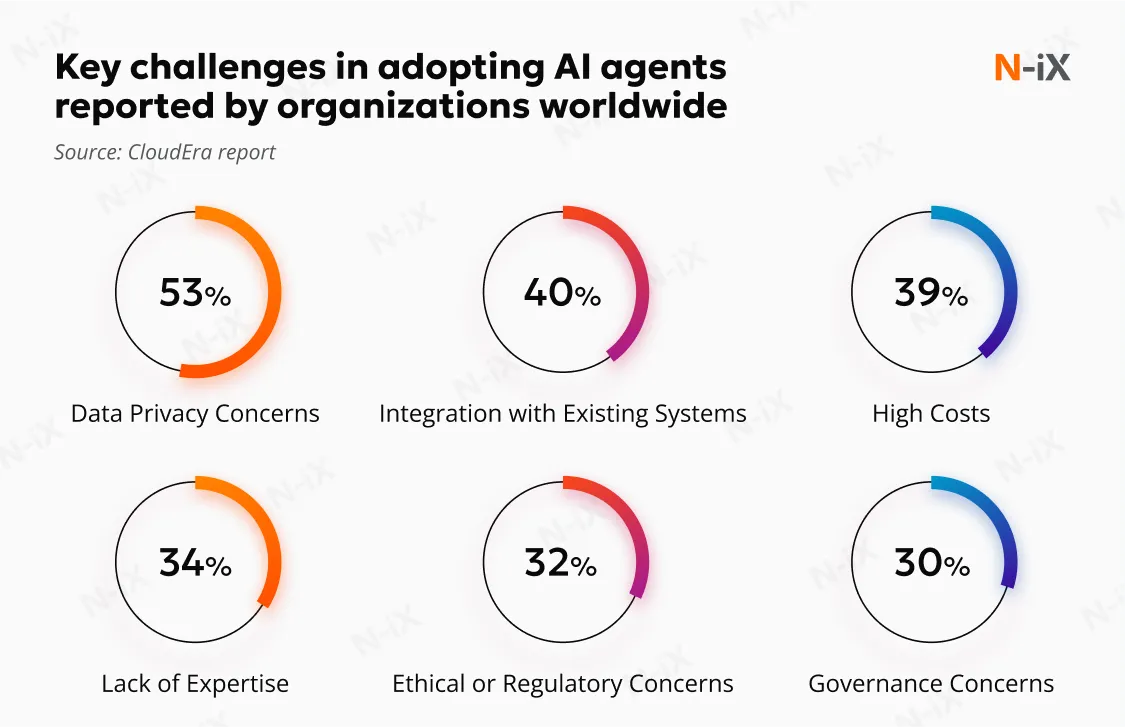
In the new CloudEra report, organizations were interviewed about the key challenges of AI agents' adoption. The top concerns they reported were data privacy (53%), integration issues (40%), high costs (39%), and lack of expertise (34%). We asked our cloud and AI experts to share their insights on how to address them. Let's review the main challenges with practical remediation tips:
1. Data privacy concerns
AI agents often need access to logs, metrics, user inputs, and potentially sensitive business data. In regulated or multi-tenant environments, this access can raise concerns about compliance requirements. Without proper defenses, agents designed for tasks like scaling or incident response could inadvertently expose or store sensitive information.
Solution from N-iX: Our experts recommend building a strong data classification framework before deploying AI agents. This means limiting agents' access to only the data they need, using data encryption, and implementing strict retention policies to ensure audit logs are kept only as long as necessary for compliance.
2. Integration issues
Organizations often operate a complex mix of legacy systems, microservices, SaaS tools, and on-prem infrastructure. Integrating AI agents into this diverse ecosystem can quickly become a logistical headache, leading to fragile connections and unreliable workflows. Poorly planned integrations also increase the risk of system downtime or troubleshooting delays.
Solution from N-iX: The key to overcoming this challenge is treating agent integration as a strategic effort. N-iX recommends creating standardized interfaces through abstraction layers and containerizing agent workflows to ensure consistency. It is also crucial to thoroughly test each integration in a sandbox environment before moving to production.
3. Security threats
Cloud environments, often shared and accessible over public networks, expose AI agents to risks such as model tampering, adversarial attacks, and unauthorized access. Malicious actors could manipulate the AI's training data or logic to produce biased or harmful outputs, or even hijack the agent for malicious purposes. Such vulnerabilities not only disrupt operations but can also damage a company's reputation and lead to significant financial losses.
Solution from N-iX: It is crucial to design a specific security strategy designed to protect the core of cloud-based AI agents. Our team recommends implementing model hardening techniques, including secure training pipelines and input validation, to prevent adversarial attacks. We also use advanced monitoring and anomaly detection algorithms to spot and block suspicious activity or unauthorized changes in real time. In addition, strict access controls and authentication protocols within a zero-trust framework ensure that only verified entities can interact with or update the AI system.
4. Lack of expertise
Deploying and operating AI agents in the cloud requires a blend of expertise in AI engineering, cloud-native architecture, and DevOps. Many organizations find their existing teams unprepared for the demands of model management, pipeline orchestration, and responsible AI practices.
Solution from N-iX: If you need immediate support on leveraging AI agents in cloud computing, consider partnering with experienced consultants. For instance, N-iX can provide you with the necessary cloud and AI expertise to accelerate your maturity model without compromising on governance or security.
How can N-iX help with leveraging AI agents in cloud computing?
AI agents are revolutionizing cloud computing, offering advanced opportunities to automate operations, optimize resources, and enhance business workflows. With expert guidance, you can confidently embrace leveraging agentic AI in cloud computing strategy, tackle challenges, and drive innovation. N-iX can help with smooth adoption as we have the necessary capabilities:
- 400+ cloud experts and 200+ AI, ML, and data specialists ready to address your specific needs;
- Completed over 60 data science and AI projects across various industries;
- Partnerships with leading cloud service providers, having the following statuses: AWS Premier Tier Partner, Microsoft Solutions Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner;
- Extended expertise in AI agent development, LLM fine-tuning, and cloud-native.
Ready to take the next step? Contact N-iX today to explore tailored AI agent solutions for your cloud transformation journey.
Have a question?
Speak to an expert