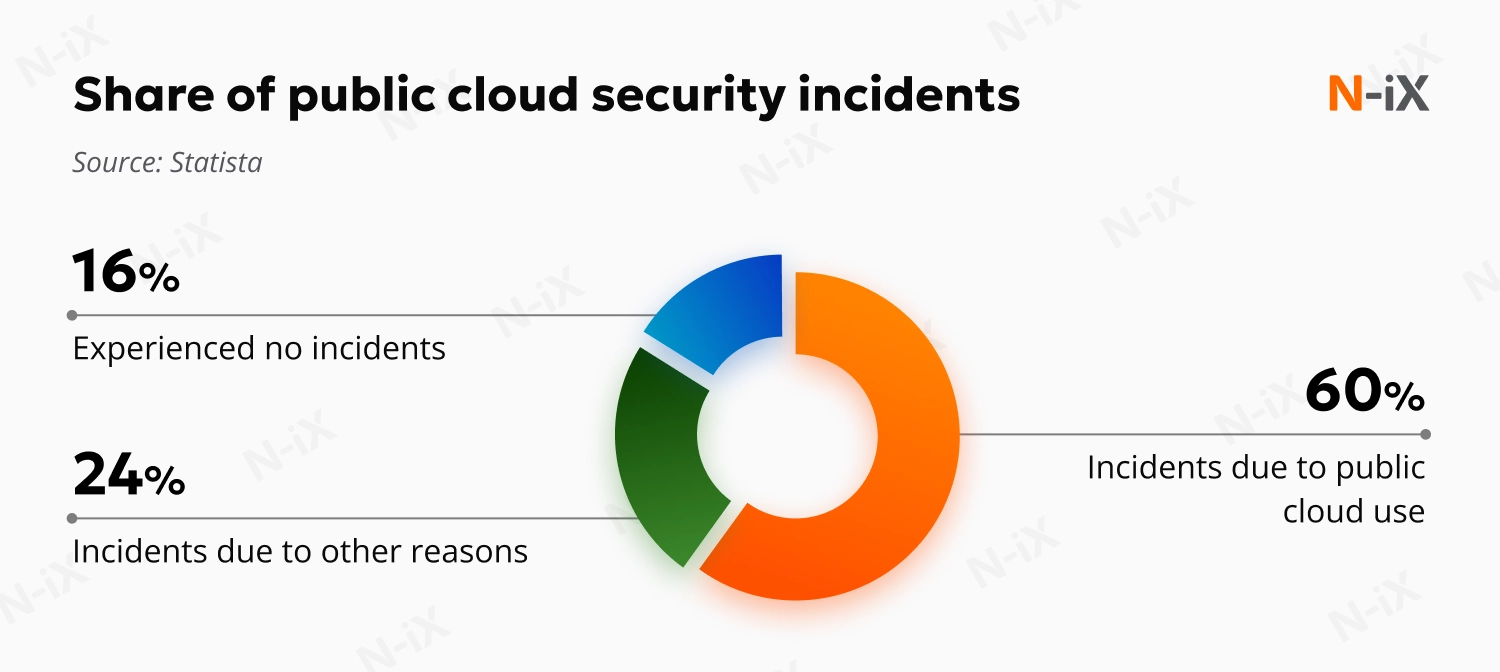
Enterprise cloud security is under more pressure than ever. Most organizations now operate across multiple clouds, expanding their capabilities but also increasing the complexity of their infrastructures. Traditional security tools were never meant to shield such vast, distributed environments. As a result, enterprise clouds often have significant gaps in protection, and malicious actors readily take advantage of them to launch targeted attacks. In fact, Statista reports that 84% of companies surveyed in 2024 fell victim to a security incident. Out of those, 60% were affected specifically due to their public cloud use.
So, how can your organization protect your cloud while keeping operations flexible and compliant? Read on and discover how to build stronger cloud security.
In this guide, we will explore:
- What cyber threats are widespread in cloud environments;
- How to build comprehensive security for your enterprise cloud;
- How the shared responsibility model affects your cloud security decisions.
Top cyber threats putting enterprise cloud security at risk
Attackers continue to develop more sophisticated techniques targeting cloud environments. N-iX security experts regularly monitor these emerging threats to help organizations strengthen their defenses. Here’s what businesses need to watch out for:
1. AI-powered cyberattacks
Cybercriminals now use Artificial Intelligence to automate complex attack chains, from vulnerability scanning to system exploitation. At the same time, they launch hyper-personalized phishing campaigns that adapt in real time. These messages can mimic tone, context, and urgency, making them difficult to detect.
Traditional security tools often fall behind, unable to face the new threats. Additionally, AI itself can introduce privacy risks. If not properly managed, it can become a source of data exposure or even a gateway for future breaches.
2. Cloud misconfigurations
Misconfigured security settings and controls pose a significant threat to cloud enterprise security. They create vulnerabilities that enable malicious actors to breach systems and access sensitive resources.
The most dangerous misconfigurations include:
- Unrestricted outbound access that allows data exfiltration;
- Disabled logging that prevents the detection of malicious events;
- Exposed access keys that can be rapidly misused;
- Excessive account permissions that expand the potential damage.
Secure your cloud with 10 best practices—get the guide now!


Success!

3. Account hijacking
Account hijacking remains one of the top threats to enterprise cloud security, and for a good reason. When attackers gain access to a valid account, they can steal data, disrupt operations, launch further phishing attempts, or move laterally within your cloud environment.
4. Vulnerable APIs and integrations
Third-party tools make cloud environments powerful. They speed up development, extend core capabilities, and enable fast innovation at scale. However, with great agility comes a great need to carefully assess the safety of each integration. APIs connecting enterprise applications to cloud services have become prime targets for attacks. When poorly secured, they can expose sensitive data or allow unauthorized access to core systems.
5. Advanced persistent threats (APTs)
APTs are long-term, targeted attacks where intruders quietly infiltrate systems to steal sensitive data over time. In cloud environments, they exploit misconfigurations, stolen credentials, or vulnerable APIs to stay hidden and move laterally. Their stealth and persistence seriously threaten cloud-based enterprise security, especially for organizations handling valuable intellectual property or regulated information.
6. Insider threats and data leaks
Not all threats come from the outside. In many cases, employees accidentally leak sensitive information by sharing files improperly, forwarding confidential data to personal email, or misusing cloud collaboration tools. Even small mistakes can lead to major breaches, especially when made by staff with high-level access.
7. Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks
DoS attacks specifically target cloud services to overwhelm systems and render them inaccessible to legitimate users. These attacks disrupt operations, cause revenue loss, and damage reputation. To effectively mitigate this threat, businesses need sufficient bandwidth and server capacity, which can be challenging to achieve in distributed cloud environments.
8. Shadow IT and unmanaged SaaS
As hybrid workplaces and remote work expand, employees often turn to unapproved apps to get things done. This growing trend, known as shadow IT, creates serious blind spots in cloud security for enterprises. Without proper oversight, these tools can bypass security protocols, expose sensitive data, and introduce vulnerabilities. Unmanaged SaaS use significantly increases the risk of breaches and compliance failures.
So, what exactly do you need to do to secure your share of assets, systems, and data?
7 best practices for building strong enterprise cloud security
Effective cloud security comes from consistent action. Our experts define seven practices at the core of creating comprehensive protection across your cloud operations.
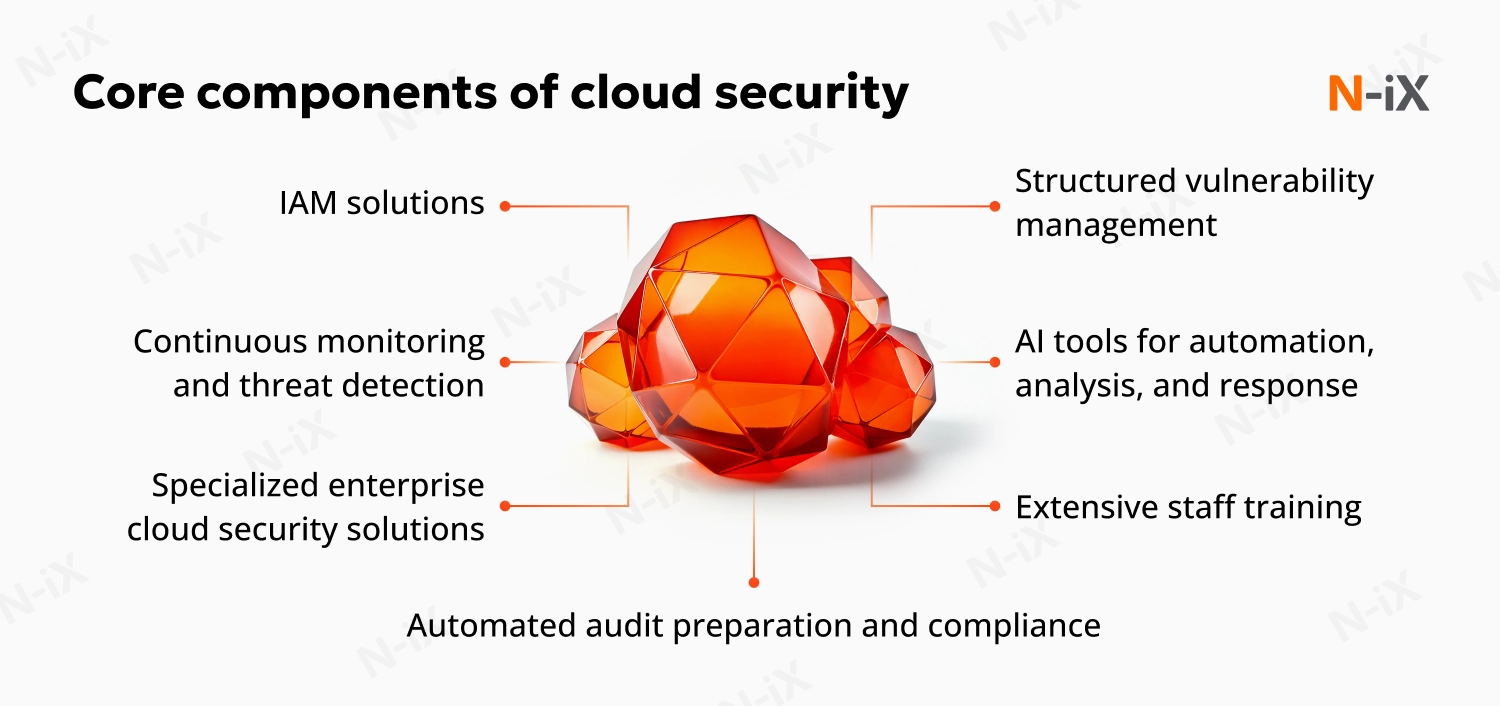
1. Implement identity and access management (IAM) solutions
A well-configured IAM system is your first line of defense against unauthorized access. The principle of least privilege should govern every access decision. This means that users should receive only the minimum permissions necessary for their specific roles. Multi-factor authentication becomes non-negotiable for all users, with administrative accounts requiring additional scrutiny and protection.
When implementing these security mechanisms, keep in mind that maintaining ease of use is equally important. N-iX experts stress that complicated procedures can stall operations and even encourage unsafe practices, such as creating weak passwords. To balance security with usability, N-iX establishes centralized identity management systems that support federated identity and single sign-on capabilities. This approach enables better oversight of user access patterns while keeping systems easily accessible for authorized users.
2. Automate compliance and audit preparation
Compliance automation transforms what was once a periodic, manual exercise into a continuous, proactive process. Tools like AWS Audit Manager and Config enable ongoing assessment against GDPR, PCI DSS, and other regulations. These solutions automatically collect evidence, generate reports, and identify compliance gaps before they escalate into violations. For organizations operating multi-account environments, automation also helps maintain consistent policies across systems while reducing manual audit preparation efforts.
3. Establish continuous monitoring and threat detection
Real-time visibility across cloud environments enables rapid anomaly detection, helping prevent breaches. However, visibility without actionable intelligence creates noise, not security. To achieve effective cloud security monitoring, N-iX experts recommend the following framework:
- Monitor across all layers: Capture data from network traffic, user behavior, application activity, and system logs to build a comprehensive security picture;
- Correlate data from multiple sources: Integrate logs and alerts into a centralized system to identify patterns and spot threats faster;
- Normalize and prioritize alerts: Filter and categorize events to reduce false positives and focus on what truly matters;
- Establish continuous audit trails: Track all user and system activity to support investigations and ensure compliance;
- Automate responses where possible: Use predefined rules or AI-driven tools to contain threats quickly and reduce response time.
4. Use AI capabilities for automation and accuracy
While cybercriminals use Artificial Intelligence for attacks, you can utilize it to strengthen defenses. In enterprise cloud security, AI helps detect threats faster by analyzing huge volumes of activity across users, systems, and applications. It spots subtle anomalies, learns from behavior over time, and accelerates response. This level of speed and precision is essential for proactive security that can keep pace with constantly evolving threats.
Tip from N-iX engineers: AI should complement, not replace, human oversight. Combine AI solutions with human-in-the-loop processes for decision-making in high-risk scenarios. This hybrid approach ensures smarter detection without compromising accuracy, especially in complex cloud ecosystems where context is key.
Read more: Top 9 use cases of AI in cloud security
5. Integrate specialized enterprise cloud security solutions
As cloud environments grow more dynamic, general-purpose security tools often fall short. To stay protected, enterprises rely on solutions that address specific security challenges. Several commonly used categories of tools include:
-
Cloud access security brokers (CASBs)
CASBs function as security policy enforcement points between users and cloud services. They provide visibility into shadow IT usage, enforce data security policies, and protect against threats. These solutions help organizations discover all cloud applications in use, assess their risk levels, and implement tailored security policies.
-
Cloud detection and response (CDR) solutions
CDR provides threat detection and response capabilities specifically designed for multi-cloud environments. These solutions use Machine Learning and behavioral analysis to identify suspicious activities and automate responses, reducing manual security-related workload. As a result, threats can be contained faster, even when human intervention isn’t immediately available.
-
Cloud security posture management (CSPM)
CSPM tools continuously monitor cloud configurations for risks and compliance issues. They detect misconfigurations, enforce best practices, and help prevent data exposure. CSPM also supports regulatory compliance by identifying policy violations early and providing clear remediation steps.
-
Cloud workload protection platforms (CWPPs)
CWPPs secure workloads across virtual machines, containers, and serverless functions. They offer runtime protection, vulnerability management, and threat detection at the workload level. These platforms help organizations monitor cloud-native workloads in real time and prevent unauthorized changes.
6. Conduct employee training to reduce human error
Human error remains the leading cause of cloud security incidents. Regular training sessions should focus on security awareness, proper configuration practices, and recognizing social engineering attempts.
Tip from N-iX security experts: Create documented security processes that all stakeholders can access and understand. Clear documentation ensures everyone knows their security responsibilities, reducing the likelihood of costly errors.
7. Design robust vulnerability management procedures
Effective vulnerability management involves continuous scanning, assessment, and remediation across your cloud infrastructure. Regular vulnerability assessments identify security weaknesses before attackers can exploit them.
Our security experts note that not all vulnerabilities pose equal risk. To ensure critical issues receive attention first, prioritize threats based on exploitability and potential business impact. This helps focus resources where they matter most and avoid overloading your teams with low-priority fixes.
Following security best practices is crucial, but it’s only one part of the equation. To secure your cloud environment efficiently, you need to understand which responsibilities are handled by the vendor and which fall on your organization.
The shared responsibility model: What enterprises must know
In traditional on-premises environments, organizations are responsible for controlling their entire security stack. Cloud solutions, on the contrary, split that accountability between vendors and customers. Cloud service providers (CSPs) ensure infrastructure security (physical hosts, storage, and networking), while organizations are responsible for protecting their data, applications, and user access.
The challenge lies in the details. Many organizations assume their cloud provider handles all security aspects, but this is a misconception. The distribution of responsibilities varies greatly across different service models, and misunderstanding these boundaries can leave critical assets unprotected.
How do responsibilities differ in IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
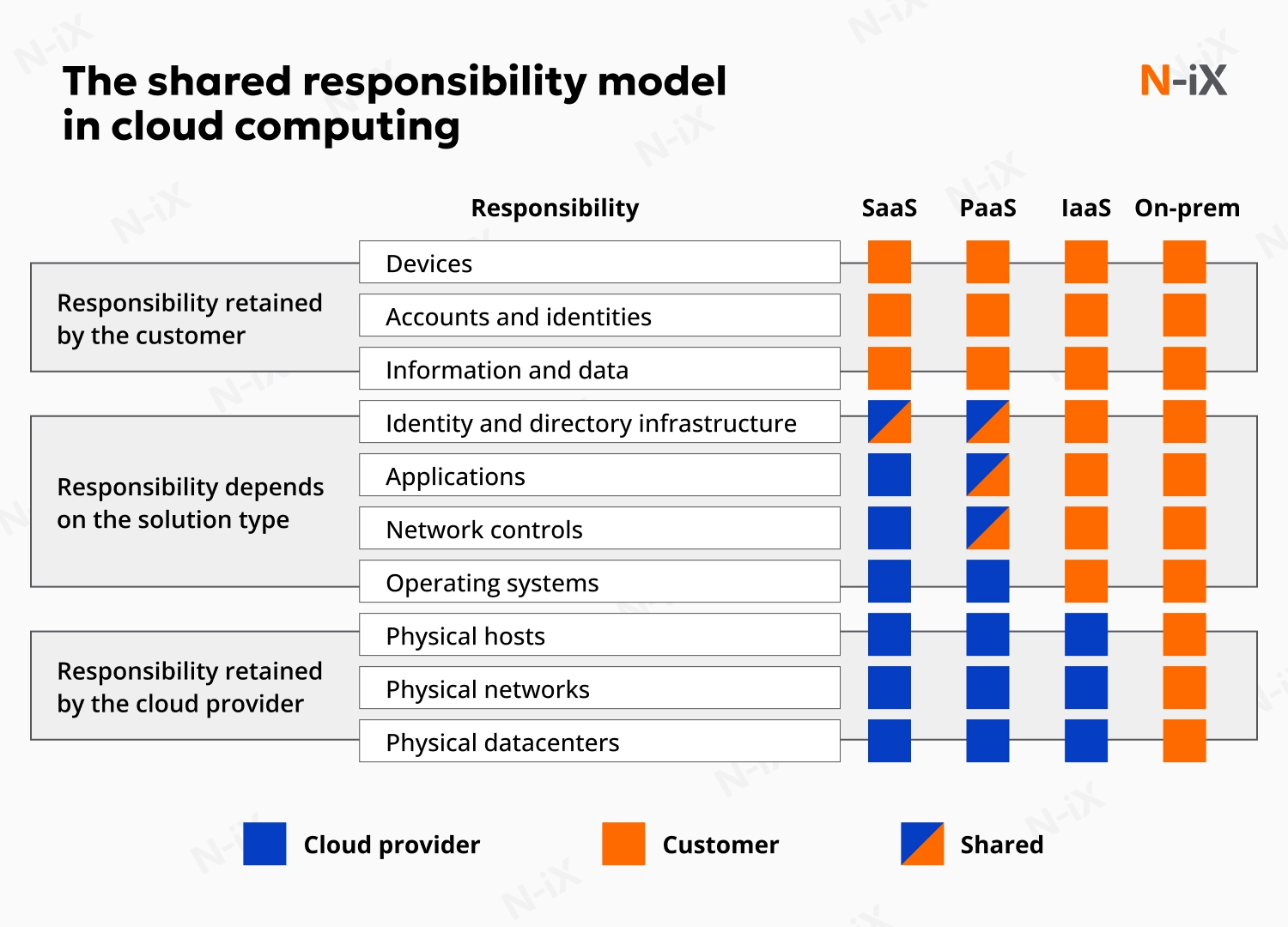
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) places the heaviest security burden on customers. While CSPs manage physical infrastructure and virtualization layers, customers must secure everything built on top. This may include operating systems, applications, middleware, data, and network configurations. This model offers maximum control but requires expertise in cloud security for enterprise.
Platform as a service (PaaS) shifts responsibilities toward the middle ground. Vendors secure both infrastructure and development platforms, but customers remain accountable for applications they build, security configurations, and data protection. This model reduces operational overhead while maintaining application-level control.
Software as a service (SaaS) assigns most security responsibilities to CSPs, who handle application-level security alongside infrastructure. However, customers still control crucial elements like data classification, user access permissions, and identity management. Even in SaaS environments, customers cannot delegate responsibility for their data and user access.
How N-iX helps you build advanced enterprise cloud security
With over 23 years of industry experience, N-iX delivers cloud cybersecurity services that protect your critical assets from today’s most sophisticated threats. Our team comprises over 2,400 specialists, including more than 400 cloud engineers, who have successfully delivered over 150 cloud and 100 security projects in the past five years.
- As an AWS Premier Tier Services Partner, Microsoft Solutions Partner, and Google Cloud Platform Partner, N-iX brings platform-specific expertise to secure your cloud infrastructure across any provider.
- We adhere to industry-leading security standards, including PCI DSS, ISO 9001, ISO 27001, and GDPR, ensuring your data remains protected throughout your cloud journey.
- Through regular risk assessments and robust security measures, we help you establish compliant, secure cloud environments that build customer trust while protecting against financial and reputational losses.
The most important step is taking action today. Discover a clear path forward and transform cloud security into a strategic advantage with N-iX.
Have a question?
Speak to an expert




