Historically, businesses could process their data on one condition. To utilize the information, you had to make it accessible. One way to achieve this is going for cloud computing. However, another problem arises. While standard cloud security protects assets at rest and in transit, the processing layer contains sensitive data visible to infrastructure providers and potential attackers. This vulnerability has created friction for critical workloads moving to the cloud, often forcing organizations to choose between privacy and innovation.
Confidential computing eliminates this problem by securing data during processing, ensuring that it remains encrypted even while in use. This technology enables more secure collaboration and better protection without relying on blind trust.
In this article, we’ll explore key confidential computing use cases and how they can be applied to secure sensitive data and workloads across industries.
What is confidential computing?
Confidential computing is a technology that protects data while it is being processed. For years, cybersecurity professionals have focused on two specific states of data: data at rest (encrypted on a hard drive) and data in transit (encrypted as it moves over a network). However, there was always a gap in the actual processing of data. To query a database, train an AI model, or calculate a credit score, it had to be decrypted in the computer’s memory.
Confidential computing closes this gap. It encrypts data while it’s in use, allowing you to process sensitive information in the cloud without exposing it in plaintext to the underlying infrastructure.
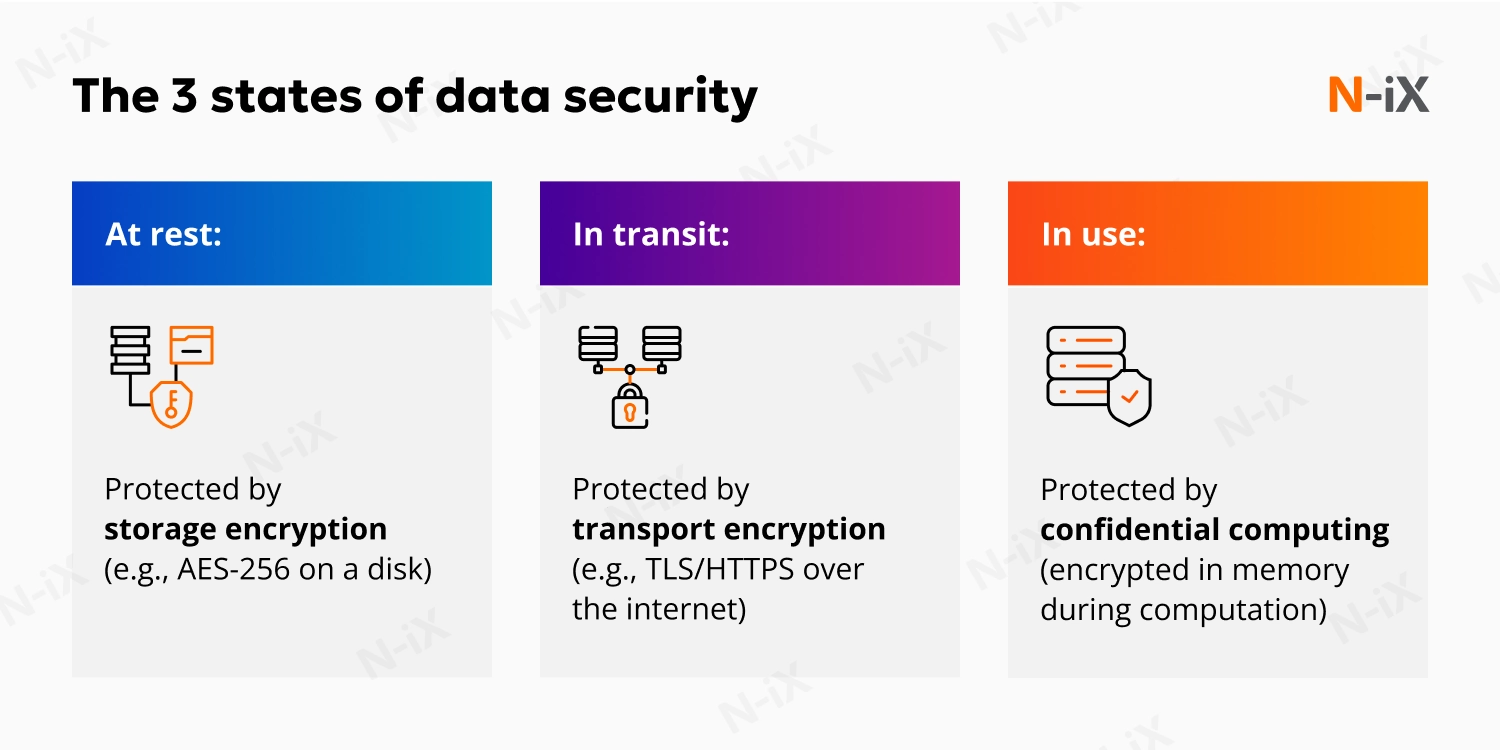
To achieve this, confidential computing uses a hardware-based capability called a trusted execution environment (TEE), often referred to as a “secure enclave.” Major cloud platforms support this model today, including Azure confidential computing, which provides hardware-backed enclaves for sensitive workloads running on shared infrastructure.
The TEE isolates your workloads from the rest of the system. Even the hypervisor, the cloud provider’s operating system, and the cloud administrators can’t see inside the enclave or access the keys. This hardware-level isolation allows you to run regulated workloads on public infrastructure while maintaining strict control over who and what can access them.
Removing the cloud provider from the access chain changes how organizations approach risk, compliance, and workload placement. Let’s explore the core confidential computing use cases and discover why this technology is essential for strong cloud security.
5 key confidential computing use cases
1. Digital sovereignty and regulatory compliance
Managing global cloud environments while adhering to local regulations such as GDPR is a complex balancing act, especially as digital sovereignty becomes increasingly crucial. While policy controls and contractual assurances are necessary, they don’t prevent privileged access at the infrastructure level. Confidential computing adds a technical control layer. By encrypting data in use, it enforces strict jurisdictional boundaries that prevent access by foreign parties, regardless of where the physical server resides.
This significantly reduces the risk of privileged cloud or infrastructure operators accessing sensitive data outside approved jurisdictions. You can implement policies ensuring that only users authenticating from specific sovereign regions can access your workloads. This capability is essential for strengthening compliance and supporting robust data governance practices across global operations.
Discover more hand-picked cloud security trends for 2026
2. Enhanced encryption and key management
Your encryption is only as strong as the protection of your keys. Attackers increasingly target memory to scrape plaintext passwords, tokens, and keys while they are exposed during processing. Confidentiality in cloud computing reinforces your key management systems (KMS) by isolating their contents in a hardware-based enclave, rendering memory-scraping attacks ineffective.
This technology also elevates Bring Your Own Key (BYOK) strategies. By using hardware security modules (HSMs) together with confidential enclaves, you can transfer keys to the cloud without the cloud provider ever having access to them. In environments such as AWS confidential computing, this approach allows organizations to combine BYOK, HSMs, and enclave-based isolation while retaining full ownership of their security perimeter.
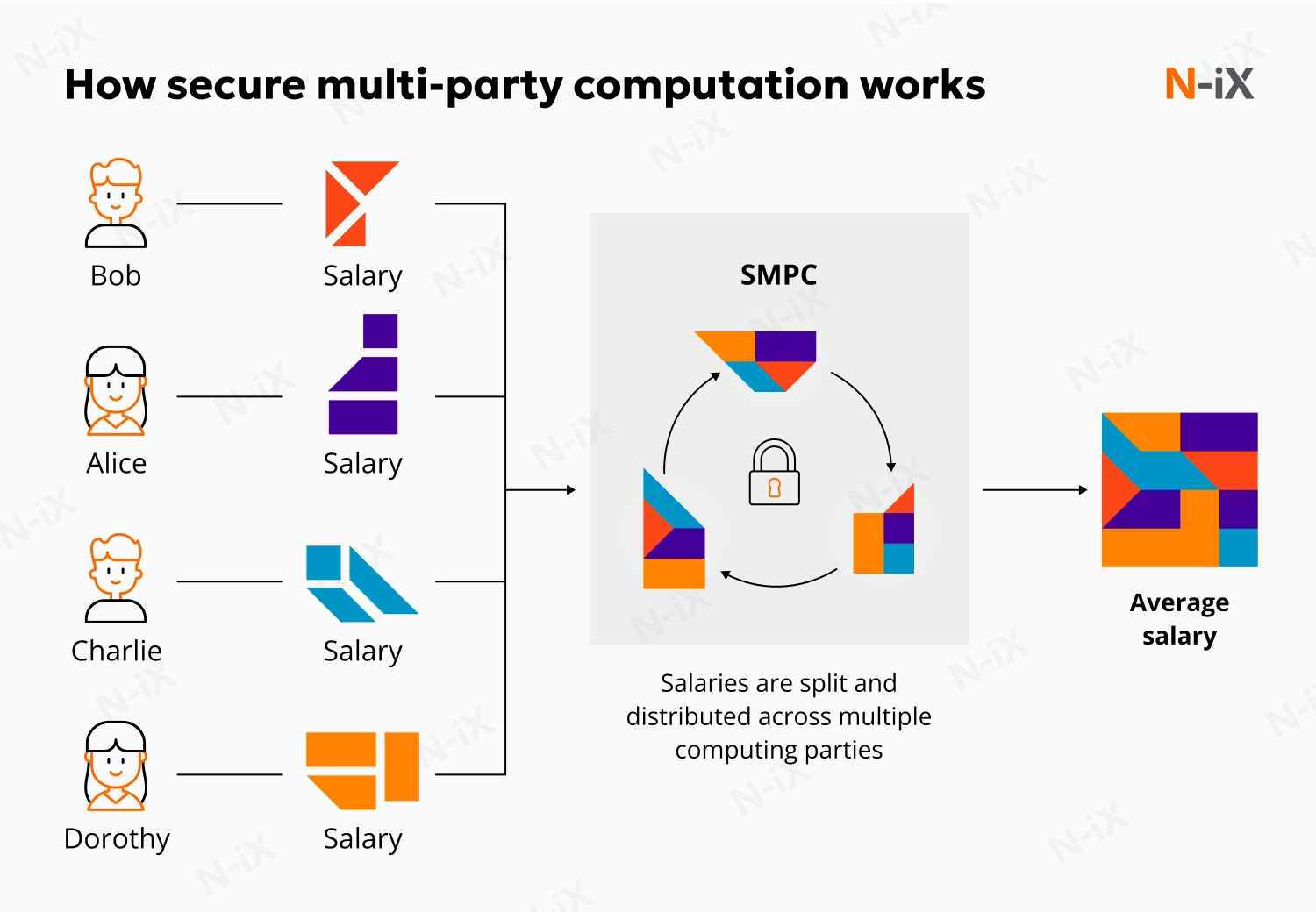
3. Secure multi-party computation
Business often requires collaboration, but making your sensitive data accessible to others can carry risk. Secure multi-party computation (SMPC) is one of the more advanced confidential computing use cases, enabling controlled joint processing of sensitive datasets. Platforms like GCP confidential computing help you combine datasets to extract mutual insights, such as fraud patterns across banks, without revealing the underlying raw data to the other party.
Our experts note that this approach directly addresses the trust gap between organizations. For example, two organizations can upload encrypted data to a single enclave within a virtual machine. The enclave processes the joint inputs and returns only the computed result, ensuring neither party (nor the cloud provider) sees the other’s upload.
4. Confidential AI and Machine Learning
As AI adoption accelerates, you face a dual challenge: protecting sensitive data used for training and safeguarding the proprietary model itself. Confidential computing enables you to aggregate sensitive datasets, such as healthcare records or personally identifiable information (PII), to train powerful models without exposing individual data points. Google Cloud confidential computing, for example, supports this approach by isolating both training data and model execution within hardware-protected environments.
Simultaneously, it protects your intellectual property. Our experts recommend running proprietary models inside a TEE to hide the weights and logic from both the infrastructure provider and the end-user. This prevents competitors or bad actors from inspecting or reverse-engineering your hard-earned algorithms while they run in production.
Tip from N-iX: The confidential cloud is becoming essential for large language models (LLMs). It allows enterprises to use hosted AI services without fearing their prompts or proprietary context data will be used to retrain the public model.
Read also: Top 7 use cases of AI in cloud security
5. Secure blockchain and digital assets
In decentralized networks, integrity is everything. Confidential computing adds a critical layer of hardware-based privacy to blockchain technologies. With platforms like Microsoft Azure confidential computing, you can protect transaction data and smart contract execution, ensuring that while the network reaches consensus, the data remains inaccessible to unauthorized validators.
This is particularly vital for crypto custody. By securing hot wallets and transaction processing logic within enclaves, you protect digital assets from both insider threats and external hackers. This ensures that signing keys never exist in plaintext memory where they could be vulnerable to exfiltration.
How different industries apply confidential computing
Industry context matters when applying confidential computing. Regulatory constraints, data sharing models, and threat exposure vary widely, shaping how this technology is adopted. The confidential computing use cases below show how different sectors apply it in real-world environments.
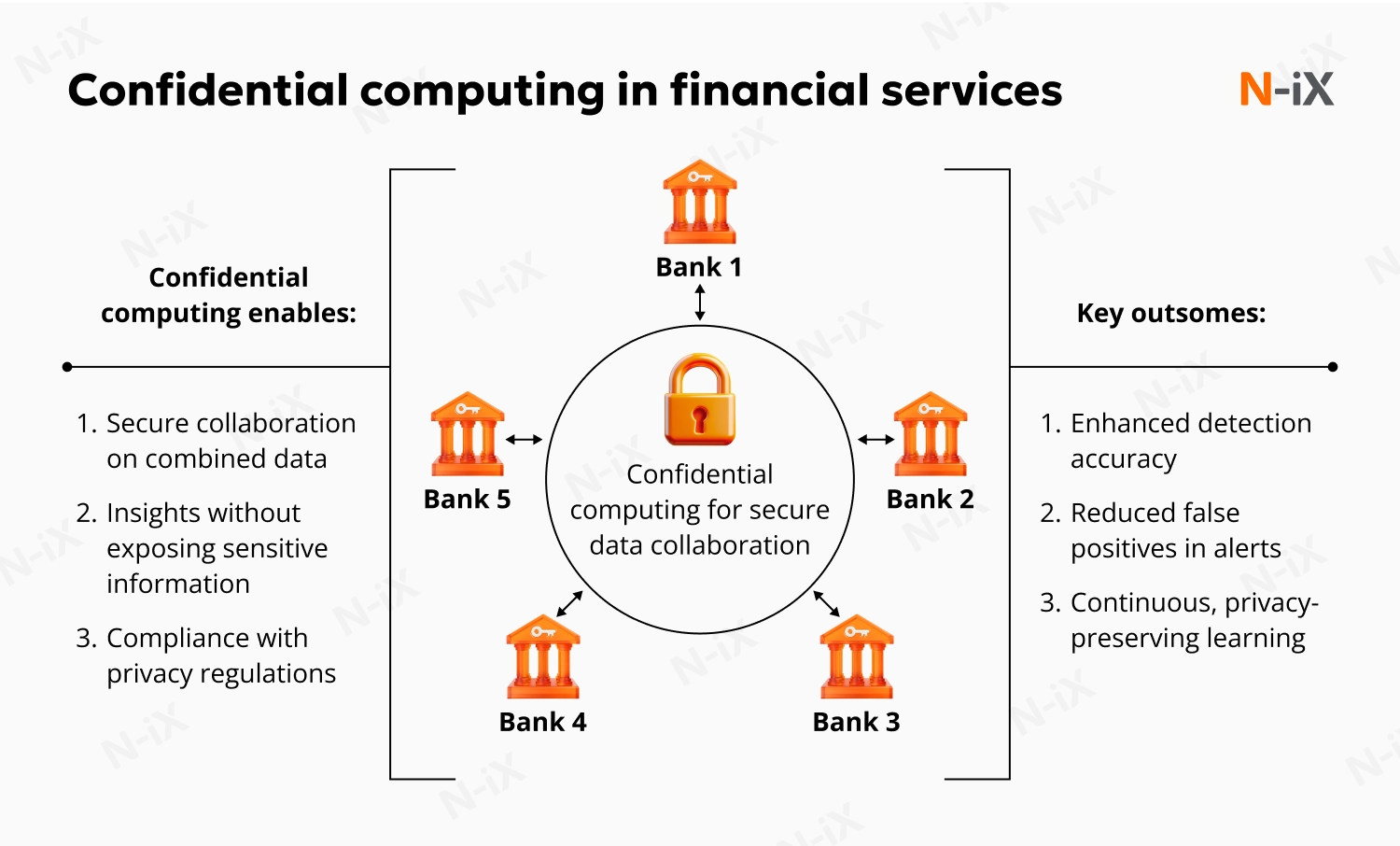
Financial services
Financial institutions face a persistent tension: they must share data to fight financial crime while adhering to strict bank secrecy and privacy laws. Confidential computing enables secure collaboration across institutions without exposing customer data or proprietary information.
In practice, this is reflected in the following use cases:
- Anti-money laundering (AML): Banks sharing transaction data to detect money laundering patterns across institutions without violating bank secrecy laws or exposing customer PII;
- Fraud detection: Analyzing combined datasets to reduce false positives in fraud alerts;
- Cloud-based Know Your Customer (KYC): Running identity verification processes, such as credit scoring, in the public cloud while keeping the underlying customer data invisible to the cloud provider;
- Insider trading prevention: Using secure multi-party computation to analyze joint data for market manipulation or insider trading signals without revealing sensitive trading positions.
Healthcare and life sciences
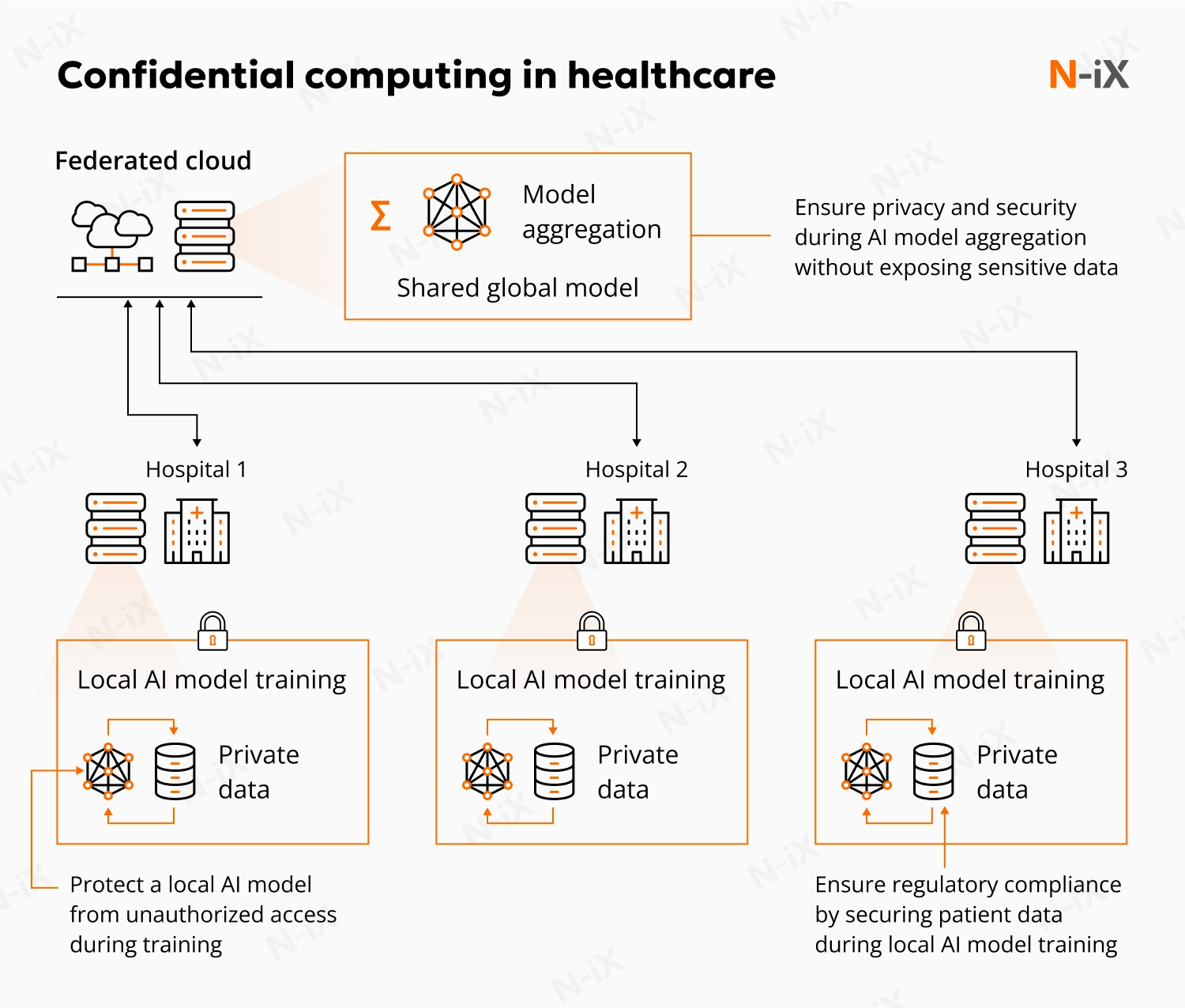
In healthcare, data silos can impede life-saving innovations, while patient privacy remains non-negotiable. By processing data inside secure enclaves, researchers and pharmaceutical companies can train AI models on aggregated datasets from multiple hospitals. This supports faster drug discovery and diagnostics without compromising patient confidentiality.
Here are several confidential computing use cases across healthcare and life sciences:
- Collaborative drug discovery: Pharmaceutical companies pooling chemical data and research to train ML models for new medications without revealing proprietary formulas;
- Privacy-preserving clinical trials: Matching patient data across multiple hospitals to identify candidates for trials while maintaining strict HIPAA/GDPR compliance;
- Federated learning for diagnostics: Training diagnostic algorithms on aggregated imagery and patient records while the data stays within the hospital’s secure environment;
- Genomic and biometric analysis: Processing highly sensitive biometric data (such as DNA sequences or forensic images) to aid investigations or personalized medicine without the risk of exposure;
- Cross-border research: Enabling researchers to analyze medical data from different countries while satisfying local data residency and sovereignty requirements;
- AI algorithm development: Accelerating the deployment of AI in healthcare by allowing algorithms to run on protected clinical data without the developer seeing the patient records.
Read more: Top 7 strategies to protect your medical data in the cloud
Manufacturing and the Internet of Things
As manufacturing becomes increasingly digitized and outsourced, protecting intellectual property (IP) is critical. The confidential cloud extends the security perimeter to the edge and to third-party factories. This way, proprietary designs and IoT telemetry remain encrypted during processing, preventing theft by contractors or administrators.
Typical applications of confidential computing in manufacturing security include:
- IP protection in outsourced manufacturing: Securely sending proprietary designs (for example, 3D print files) to third-party factories;
- Smart building optimization: Analyzing occupancy, temperature, and badge-swipe data to optimize energy usage without tracking each person’s movements;
- IoT device security: Running workloads inside TEEs on edge devices (like smart city sensors or medical equipment) to protect collected data and credentials from tampering;
- Supply chain telemetry: Analyzing defect rates and manufacturing telemetry from multiple suppliers without exposing trade secrets or competitive data;
- Critical infrastructure defense: Protecting control systems and sensitive data in high-risk environments to ensure integrity even if the broader infrastructure is compromised.
Advertising and marketing
Confidential computing enables secure, controlled processing of first-party data across organizations. Brands and publishers can match datasets and generate insights without directly sharing raw user information.
Several prominent confidential computing use cases for marketing include:
- Secure audience segmentation: Collaborating in isolated execution environments to build customer personas and insights without sharing raw user lists or PII;
- Privacy-preserving targeted ads: Delivering personalized recommendations and advertisements based on combined datasets while keeping consumer identities encrypted;
- Cross-party data activation: Enabling partners to activate shared data insights for marketing campaigns without direct data exchange;
- Customer journey analysis: Tracking user interactions across different platforms to understand the full customer journey without violating privacy regulations.
Government and public sector
Public sector agencies operate under the highest stakes, requiring data sovereignty and protection against advanced external threats. Confidential cloud computing enables governments to process sensitive workloads while enforcing jurisdictional controls and without extending trust to the cloud provider.
Common use cases include:
- Digital identity protection: Protecting citizens’ digital identities from cloud providers and rogue administrators;
- Digital forensics: Securely processing sensitive datasets for investigations while protecting the privacy of unrelated individuals and records;
- Data sovereignty enforcement: Using technical safeguards to ensure data processing occurs only within specific sovereign regions, preventing foreign access;
- Defense and intelligence: Protecting classified data and critical infrastructure information from cyber attacks, even on public cloud infrastructure;
- Secure inter-agency collaboration: Enabling different government agencies to share and analyze data jointly without compromising their respective security perimeters.
What’s next? Bring confidential computing to your cloud with N-iX
Confidential computing is no longer just a niche privacy tool; it’s the foundation for the next generation of secure cloud architecture. By protecting data in use, organizations can finally move their most sensitive workloads to the public cloud without compromising security. However, implementing trusted execution environments requires navigating complex architectural choices.
N-iX helps organizations bridge this gap by designing secure cloud infrastructures that seamlessly integrate confidential computing into your existing stack. Whether you need to secure a GenAI pipeline or build a multi-party data clean room, our experts ensure your transition to this model is compliant, scalable, and future-proof.
Why choose us:
- 23 years of experience and over 2,400 technology professionals on board;
- 400+ cloud experts and 270+ specialists holding recognized cloud certifications;
- Over 250 cloud and security projects completed within the last five years;
- Compliance with GDPR, PCI DSS, ISO 27001, ISO/IEC 27701:2019, CyberGRX, FSQS, and more;
- Extensive partnerships: N-iX holds the status of a Solutions Partner in the Microsoft AI Cloud Partner Program, AWS Premier Tier Partner, and Visual Intelligence Expertise within Google Cloud Partner Advantage.
Have a question?
Speak to an expert